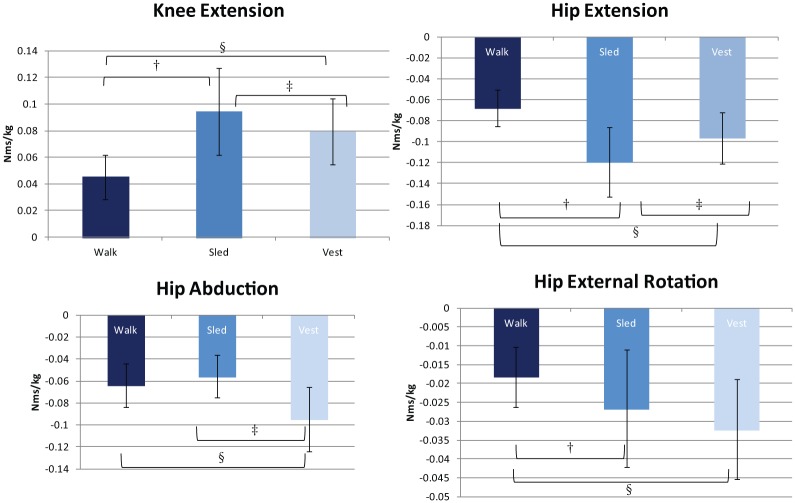
Figure 4.
Knee and hip kinetic illustrate task differences for men, with data collapsed for limb. †Significant difference between walk and sled tasks: knee extension moments (mean difference [x], −0.049; P < 0.001; 95% CI, −0.061 to −0.037), hip extension moments (x, 0.052; P < 0.001; 95% CI, 0.036 to 0.068), and hip external rotation moments (x, 0.008; P = 0.017; 95% CI, 0.002 to 0.015). §Significant difference between walk and vest tasks: knee extension moments (x, −0.034; P < 0.001; 95% CI, −0.042 to −0.026), hip extension moments (x, 0.029; P < 0.001; 95% CI, 0.018 to 0.039), hip abduction moments (x, 0.031; P < 0.001; 95% CI, 0.023 to 0.038), and hip external rotation moments (x, 0.014; P < 0.001; 95% CI, 0.010 to 0.018). ‡Significant difference between sled and vest tasks: knee extension moments (x, 0.015; P = 0.025; 95% CI, 0.002 to 0.028), hip extension moments (x, −0.023; P = 0.046; 95% CI, −0.046 to 0.000), and hip abduction moments (x, 0.039; P < 0.001; 95% CI, 0.030 to 0.048).