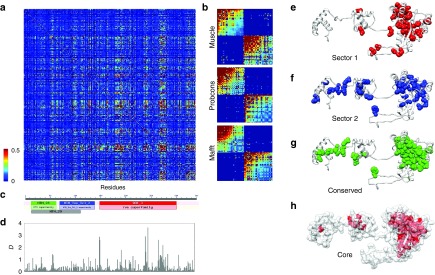
Figure 1.
Identification of sectors and conserved domains in the Sleeping Beauty (SB) transposase. (a) Statistical Coupling Analysis (SCA) matrix for the muscle alignment of 289 homologous sequences present in RepBase (+SB). The matrix represents correlations between amino acid frequencies at each position of the alignment, i.e., residue pairs that coevolve. (b) Cleaned SCA matrices for three alignments made with muscle, probcons, and mafft aligners, containing the residues of the two sectors. Residues within sectors show correlated evolution, while there is almost no correlation between sectors. (c) The transposase contains three Pfam conserved domains; two HTH domains with DNA binding functions, and a DDE domain with endonuclease activity. (d) The distribution of conservation scores (D) across the sequence. (e,f) The location of the two sectors identified with the muscle alignment in the tertiary structure of the SB transposase. The sectors are located across secondary structure elements, and are less compact than the ones reported so far, possibly due to the low sequence similarity in the alignments. Both sectors have residues in multiple conserved domains; most notably sector 2, which has residues in all three Pfam domains of the protein. (g) The location of the conserved residues (D > 0.5, muscle alignment, see also Supplementary Table S2) of the transposase. (h) The residues of the protein core. All residues with relative solvent accessibility below 0.1 are highlighted with red.