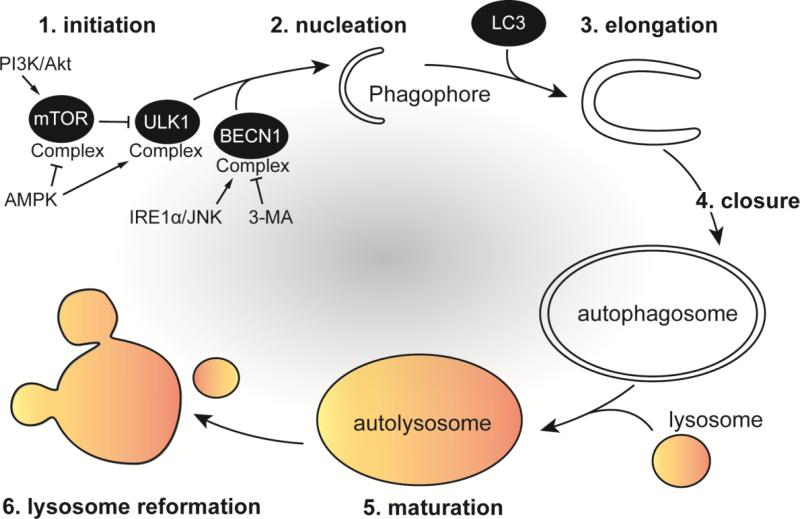
Figure 1. Sequential steps of canonical autophagy.
In the presence of amino acids, growth factors and energy, the mTOR complex represses autophagy by inhibiting the kinase activity of ULK1. The PI3K/Akt pathway inhibits autophagy, while AMPK activates autophagy by controlling mTOR activation under nutrient-limiting conditions. Upon autophagy induction (1), the ULK1 complex activates the BECN1/VPS34 complex to initiate (2) phagophore formation and nucleation. BECN1 can be activated directly by the IRE1α/JNK pathway or inhibited by the pharmacological drug 3-methyladenine (3-MA). Phagophore elongation (3) proceeds to engulf and sequester autophagic cargo and the phagophore membrane acquires LC3. Ubiquitin-like conjugation systems mediate the closure of the autophagosome (4). Maturation of the autophagosome (5) occurs via fusion with late endocytic/lysosomal compartments, forming the autolysosome where material is degraded. Autolysosomes are then recycled in a process that allows for lysosome reformation (6).