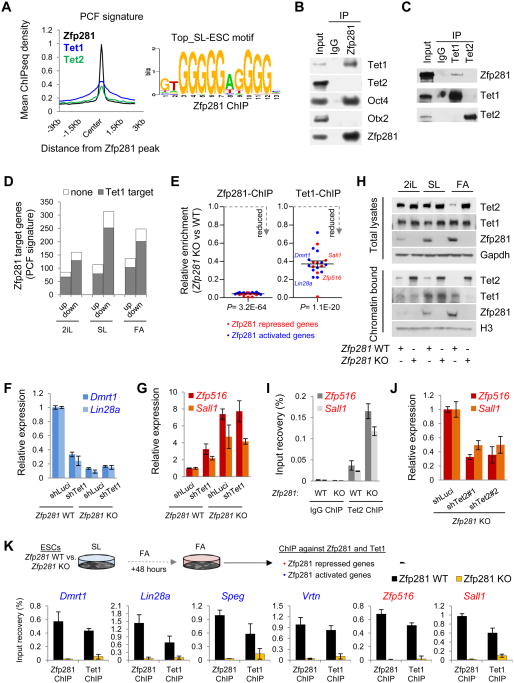
Figure 6. Distinct Functions of Tet1 and Tet2 in Modulating Zfp281-Mediated Transcriptional Control. See also Figure S6.
(A) Average ChIP-seq read density of Zfp281, Tet1, and Tet2 near the Zfp281 peak center on PCF genes (left) and the top Zfp281 binding motif in SL ESCs (right).
(B) Zfp281 interacts with Tet1 and Oct4, but not Tet2 or Otx2 in SL ESCs. IP was performed using anti-Zfp281 antibody followed by western blotting with indicated antibodies.
(C) Zfp281 interacts with Tet1, but not Tet2, in SL ESCs. IP was performed using anti-Tet1 and anti-Tet2 antibodies followed by western blotting with indicated antibodies.
(D) Comparison of Zfp281-regulated PCF gene targets with Tet1 targets showing the majority of Zfp281-regulated PCF target genes that are mis-regulated in Zfp281 KO ESCs are also Tet1 targets during pluripotent state transitions.
(E) Validation of Zfp281-dependent Tet1 binding to the target genes by ChIP-qPCR. Error bars indicate average ± SEM (n=20). P values were determined by Student's unpaired t test.
(F) Zfp281-dependent transcriptional activation function of Tet1. Error bars indicate average ± SEM (n=3).
(G) Zfp281-dependent transcriptional repression function of Tet1. Error bars indicate average ± SEM (n=3).
(H) Western blot analysis of total and chromatin-bound Zfp281, Tet1, and Tet2 levels in Zfp281 WT and KO cells cultured in SL, 2iL, or FA for 48 hours.
(I) Analysis of Tet2 enrichment at the Zfp281 repressed loci (Zfp516 and Sall1) in the presence (WT) and absence (KO) of Zfp281 in SL ESCs. Error bars indicate average ± SEM (n=3).
(J) Knockdown of Tet2 partially rescues Zfp516 and Sall1 upregulation in Zfp281 KO ESCs under SL culture condition. Error bars indicate average ± SEM (n=3).
(K) Zfp281-dependent binding of Tet1 to the candidate target genes under FA condition by ChIP-qPCR.