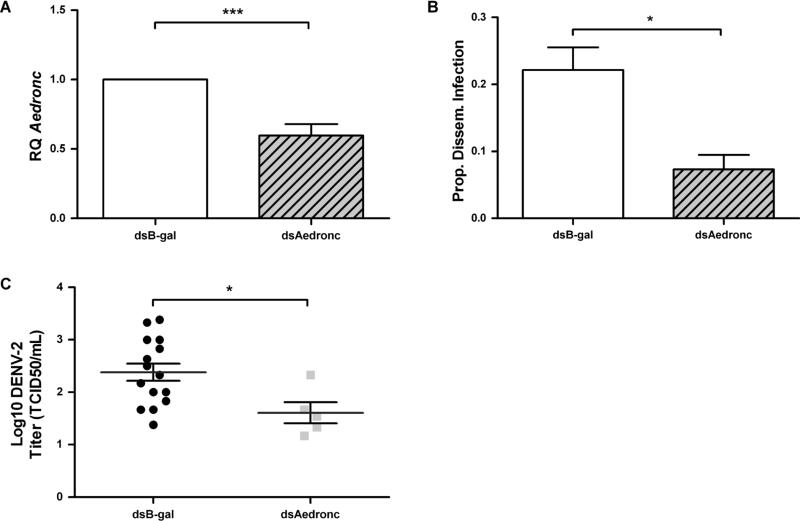
Fig 3. Aedronc knockdown decreases the proportion of mosquitoes infected and DENV-2 titer among infected individuals.
Refractory (MR) females 2-3 days post eclosion were injected with either dsAedronc or dsB-gal and: (A) tested for knockdown of Aedronc by qRT-PCR 48 h post injection (HPI). Expression is represented as Relative Quantitation (RQ) compared to dsB-gal-treated females (n=5 replicates; 5 pooled females per replicate). (B) 48 HPI, females were provided DENV-2 JAM1409-supplemented artificial blood meals. Mosquitoes were collected at 14 d PBM and tested for disseminated infection by RT-PCR of DENV RNA from leg tissue (n=3 replicates; no. infected females/total tested per replicate: B-gal: 7/30; 12/44; 9/57; Aedronc: 4/38; 3/36; 1/32). (C) Mosquitoes were homogenized in cell media, and infectious titer was measured by TCID50 assay (n=2 replicates). Error bars represent standard errors of means from biological replicates. Statistical analyses were performed using (A-B) Student's t-test or (C) Mann-Whitney U test. *p<0.05; ***p<0.001.