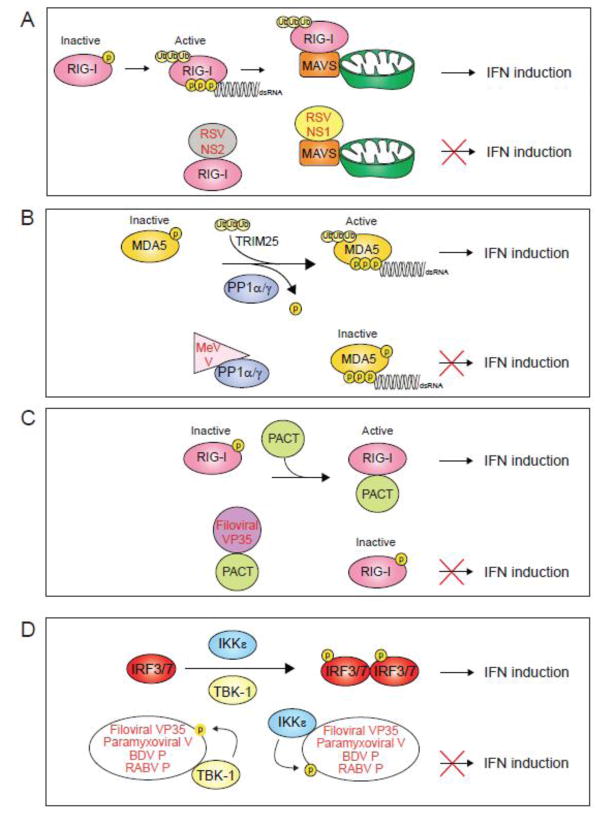
Figure 5. Mechanisms of NNSV mediated inhibition of IFN induction.
A. The non-structural proteins NS1 and NS2 from respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) interact with MAVS and RIG-I, respectively, to disrupt RLR signaling. B. Measles virus (MeV) V protein binds to protein phosphatase 1 α/γ (PP1α/γ) and inhibits dephosphorylation and activation of RLRs. C. Ebolavirus VP35 (EBOV VP35) protein binds to PACT and inhibits PACT-induced activation of RIG-I. D. Filoviral VP35 proteins bind to kinases TBK1 and IKKe and act as decoy substrates to inhibit the phosphorylation of IRF3/7. Paramyxoviral V protein and Bornavirus and Rhabdovirus P protein also inhibit IRF3/7 phosphorylation in a similar manner.