Figure 8. Viral modulation of host ubiquitination.
[70]
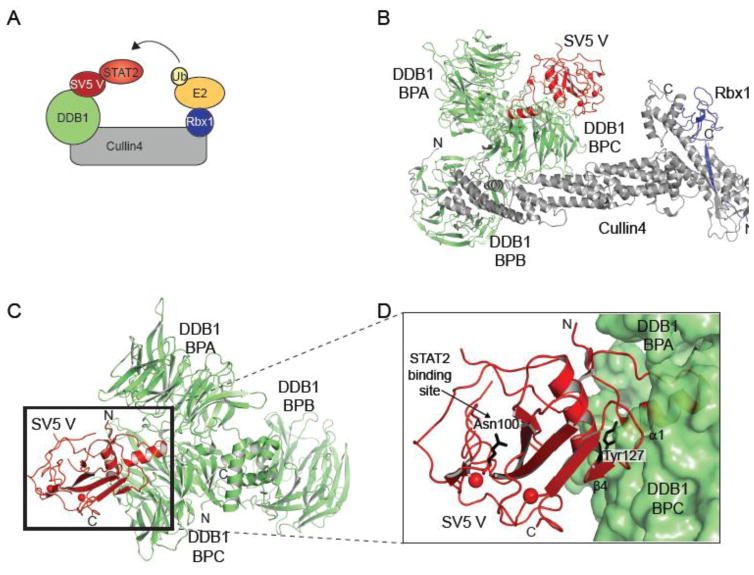
A. Cartoon model depicting the mechanism of SV5 V protein mediated ubiquitination of STAT2. B. Crystal structure of the complex of SV5 V protein (red), DDB1 (green), Cullin4 (grey), and Rbx1 (Blue) (PDB 2HYE) [118]. BPB of DDB1 binds to the N-terminal domain of Cullin4, while Rbx1 binds to the C-terminal domain of Cullin4. C. Crystal structure of Simian virus 5 (SV5) V protein (red) and DDB1 (green) showing the three β-propellers BPA, BPB, and BPC (PDB 2B5l) [117]. The SV5 V protein binds at a pocket within the BPA and BPC. D. Close up of the V binding pocket. N-terminal helix α1 of V protein inserts into the hydrophobic pocket of DDB1. Tyr127 of V protein makes important inter-subunit interactions with BPC.