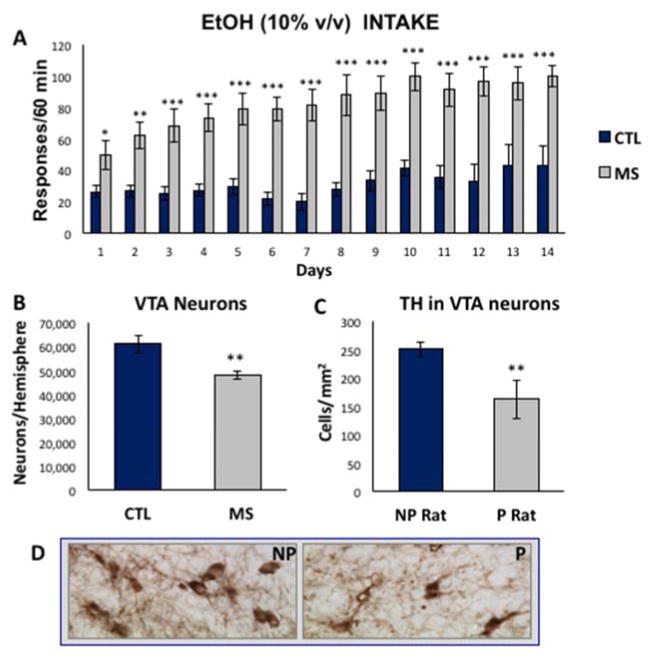
Figure 2. Increased alcohol drinking and reduction of VTA neurons in MS adult rats, similar to P rats.
A) Compared to control SD rats (blue), MS rats (gray) trained to lever press for 10% alcohol on an FR4 schedule exhibit sustained increased levels of alcohol drinking during 14 days of access, n=10 per group. B) Stereological analysis of P70 adult rat VTA showed a reduction in the number of dopamine-like neurons in animals exposed to early postnatal (P2–P21) MS, n=6 per group. C) TH-immunoreactivity in the VTA of alcohol-preferring (P) rats revealed a reduction of large TH+ dopaminergic neurons, n=8 per group. D) Representative images of TH+ immunoreactivity in the VTA of P and NP animals. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01, p<0.001.