Figure 4.
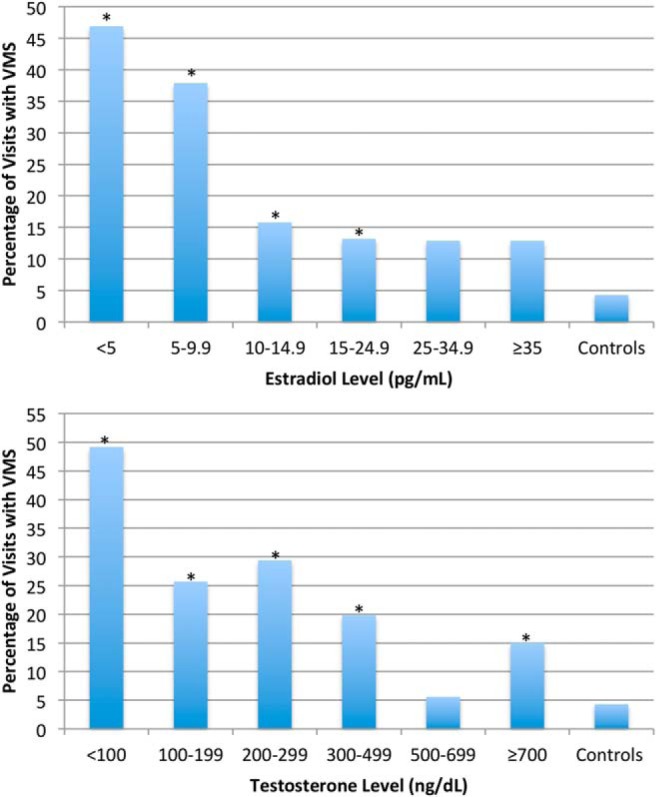
Percent of visits at which men in cohort 1 reported VMS according to their mean serum estradiol (upper panel) and testosterone (lower panel) levels from weeks 4 to 16. The percentage of visits with incident VMS in the controls is also shown. The incidence of VMS decreased significantly as estradiol levels rose from 5–9.9 to 10–14.9 pg/mL. For testosterone, the incidence of VMS decreased significantly as serum levels rose from less than 100 to 100–199 ng/dL and again from 300–499 to 500–699 ng/dL. Groups with an asterisk differed significantly from the controls. For each estradiol level group, number of visits with VMS over total visits: 82/175 for les than 5 pg/mL, 67/177 for 5–9.9 pg/mL, 15/95 for 10–14.9 pg/mL, 15/114 for 15–24.9 pg/mL, 8/62 for 25–34.9 pg/mL, 9/70 for more than or equal to 35 pg/mL, and 6/140 for controls. For each testosterone level group, number of visits with VMS over total visits: 97/197 for less than 100 ng/dL, 26/101 for 100–199 ng/dL, 30/102 for 200–299 ng/dL, 23/116 for 300–499 ng/dL, 4/72 for 500–699 ng/dL, and 16/107 for more than or equal to 700 ng/dL.
