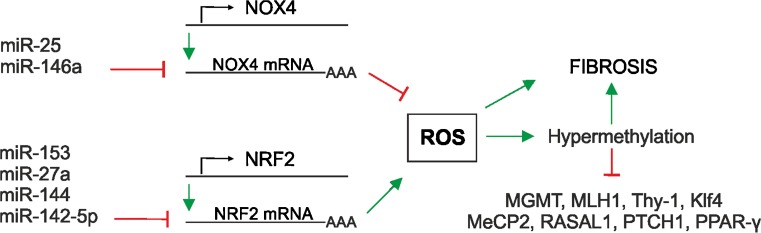
Fig. 5.
Fibrosis and ROS are interconnected with microRNA (miRNA) expression and epigenetic modifications. Several miRNAs affect cellular ROS levels via the post-transcriptional degradation of NOX4 and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2) mRNA. In addition, epigenetically, ROS-associated DNA hypermethylation contributes to the reduced expression of various genes, among them O-6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT), mutL homologue 1 (MLH1), thymocyte differentiation antigen-1 (Thy-1), Krüppel-like factor 4 (Klf4), methyl CpG binding protein 2 (MeCP2), RAS protein activator 1 (RASAL1), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR-γ) and patched1 (PTCH1)