Figure 1.
Compound Heterozygous Variants in UBA5
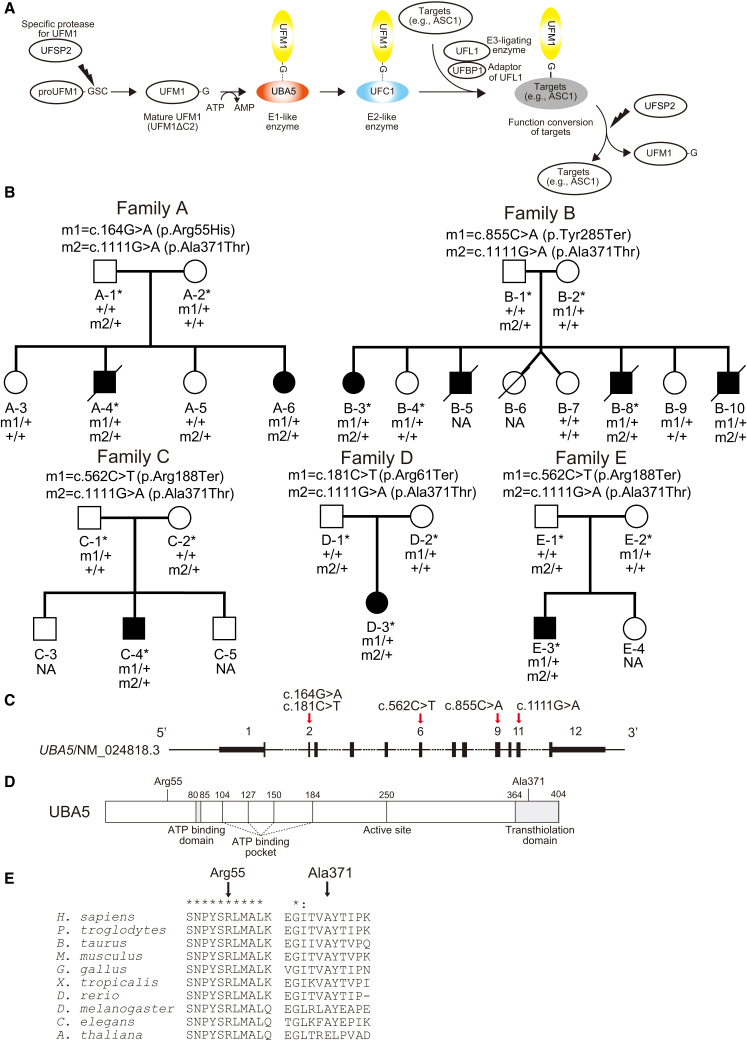
(A) A schematic of the UFM1 ubiquitin-like modifier cascade. UFM1 is synthesized in a precursor form and cleaved at the C terminus by specific protease, UFSP2.3 The E1-like enzyme UBA5 activates mature UFM1 (UFM1ΔC2), forming a high-energy thioester bond. The activated UFM1 is then transferred to an E2-like (conjugating) enzyme, UFC1, through a similar thioester linkage.4 Finally, UFM1 is covalently conjugated (ufmylated) with cellular proteins such as UFM1-binding protein 1 (UFBP1, official symbol DDRGK1) and a nuclear receptor coactivator, ASC1 (official symbol TRIP4) via UFL1 (E3-ligating enzyme).5, 6 The conjugates are cleaved by UFSP2,3 implying the reversibility of the UFM1 conjugating system.
(B) Pedigrees of five families with biallelic variants in UBA5. Variants present in each family are shown above the pedigrees. Exome-sequenced individuals are marked with asterisks. Plus sign (+) indicates wild-type.
(C) A schematic of the exon structure of UBA5 showing the locations of the variants.
(D) A schematic of the domain structure of UBA5 protein.
(E) ClustalX alignment of the Arg55 and Ala371 residues of UBA5 in metazoa and plants. Asterisks (∗) and colons (:) indicate fully conserved and highly conserved residues, respectively.