Fig. 3.
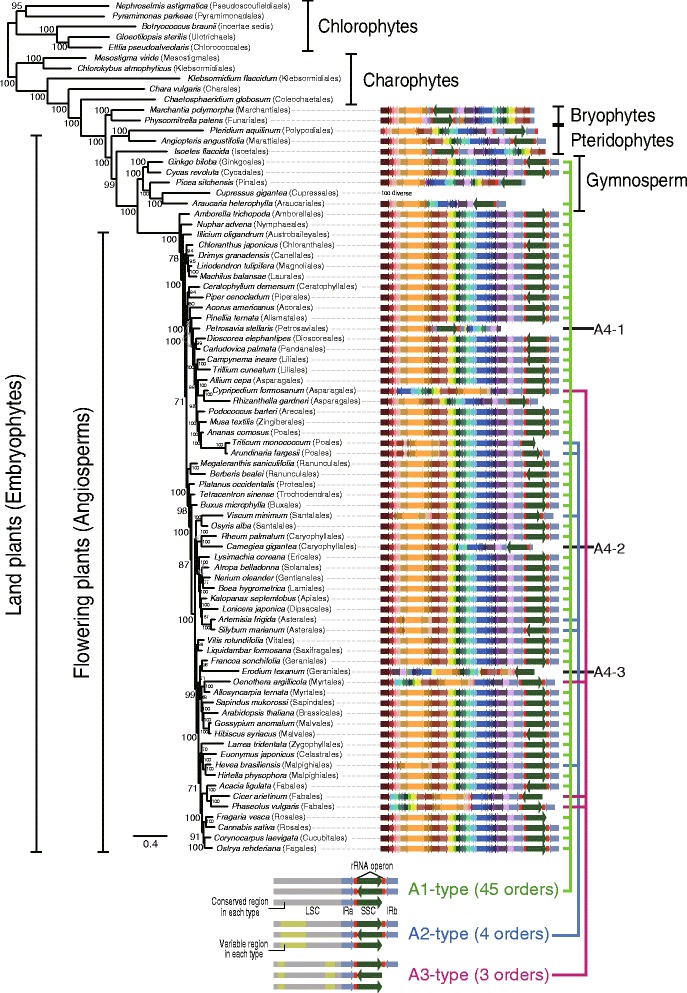
Synteny of the three major (A1–A3) and one independent (Rest) type of plastid genome architecture in the Viridiplantae. In this diagram of the A1-type (45 orders), A2-type (four orders), A3-type (three orders), and the Rest-type (three orders) in the seed plants, the shared colors indicate homologous plastid regions. The red rectangular boxes indicate ribosomal DNA operons and the red boxes and their flanking light blue arrows indicate inverted repeat (IR) regions. Between the IR regions, the dark green arrow indicates the small single copy region in plastid genomes. Each color indicates a conserved genomic fragment. Under the tree, a simplified synteny image of the three types plastid genomes are shown, whereby the gray regions indicate conservation and light green indicates variable regions
