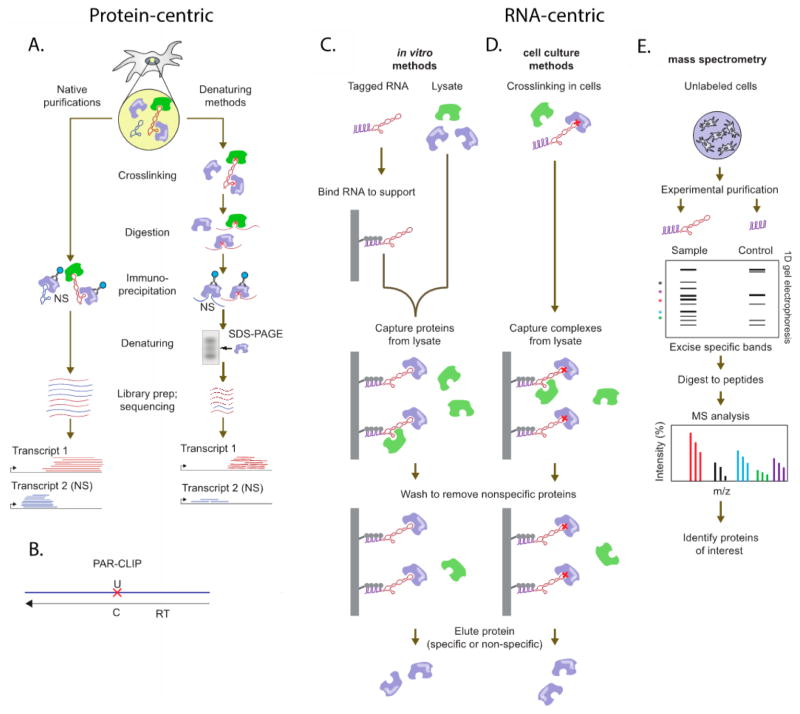
Figure 2.
RNA- and protein-centric immunoprecipitation assays. (A) Protein-centric pull-down to identify RNA–protein interactions, using either native or denaturing methods. After immunoprecipitation, transcripts are separated and submitted for sequencing. (B) A schematic of PAR-CLIP, where the red X indicated the point mutation inserted during reverse transcription (RT). (C) In vitro methods of RNA-centric pull-downs to identify RNA-binding proteins (D) cell culture methods of RNA-centric pull-downs (E) RNA:protein complexes from (C) and (D) are separated, and proteins are submitted for proteomics. Reprinted (adapted or reprinted in part) with permission from ref 77. Copyright 2015 Nature.