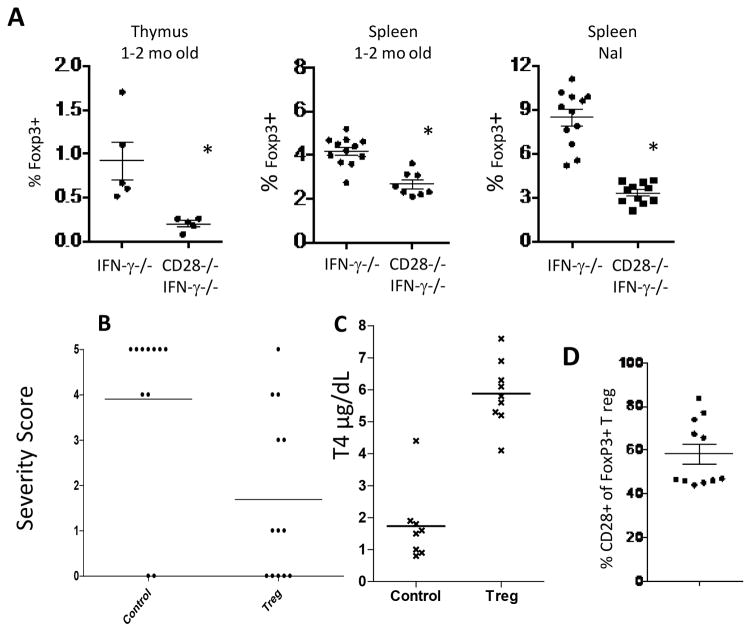
Figure 3.
IFN-γ−/− CD28−/− NOD.H-2h4 mice have fewer Tregs than CD28-positive IFN-γ−/− mice, and CD28-positive Tregs suppress TEC H/P in CD28−/− mice. A, Foxp3+ CD4+ T cells in thymus and spleens of CD28−/− and CD28-positive IFN-γ−/− mice were determined by flow cytometry. Treg numbers are significantly lower (p <0.05) both for naïve CD28−/− mice and for CD28−/− mice with TEC H/P (NaI group) compared to CD28-positive mice. B, IFN-γ−/− CD28−/− females, 6 wk of age, were irradiated (300Gy) and injected i.v. with control GFP-negative cells or sorted Foxp3+Tregs from Foxp3-GFP CD28-positive mice. Mice were given NaI water. 3 wk later, they received a second injection of sorted GFP+CD28+ Tregs or control GFP-negative cells. Thyroids were removed 4–5 wk after the second injection of Tregs. Results are representative of three independent experiments. Recipients of CD28-positive Tregs developed less severe TEC H/P (p< 0.0001) compared to recipients of Foxp3-negative T cells. N= 11 (control) and 12 (Treg recipients). C, CD28−/− recipients of CD28-positive Tregs have normal serum T4 levels while recipients of non-Treg cells have low serum T4 levels. T4 results are from some of the mice in Fig. 3B. T4 values for recipients of Foxp3+ Tregs are significantly higher than for recipients of non-Tregs (p< 0.0001). N= 8 (control) and 9 (Treg). D, Persistence and expansion of transferred CD28+ Tregs in CD28−/− mice. Sorted Foxp3+ cells from Foxp3GFP CD28-positive mice were transferred to CD28−/− mice as in B. Mice were given NaI water and GFP+ (Foxp3+) CD28+CD4+ T cells in the spleen were enumerated by flow cytometry 6–8 wk after transfer. Many T regs in recipient spleens were of donor origin. No GFP+ cells were detected in CD28−/− mice not given Tregs (not shown). Results are representative of 2 separate experiments. N = 11.