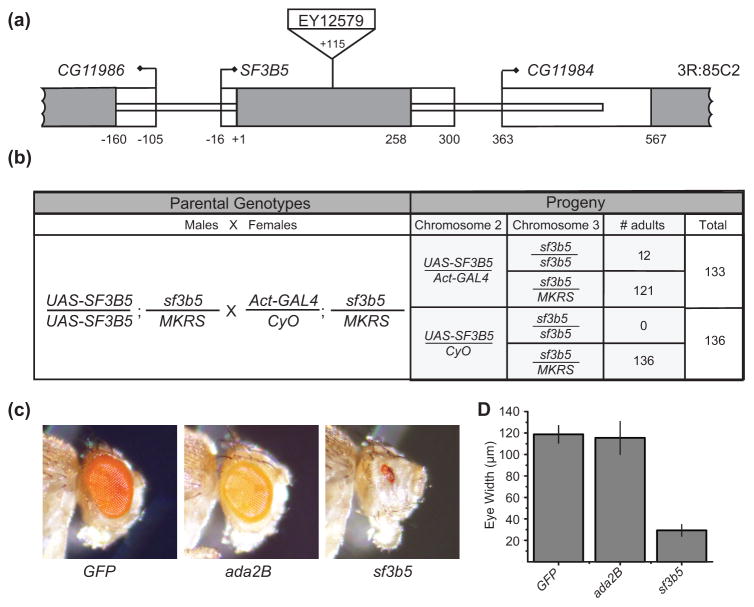
Fig 4. SF3B5 is necessary for organismal and cell viability.
(a) Schematic representation of the SF3B5 (CG11985) locus on chromosome 3R showing the position of the P-transposon EY12579. The single exon of the SF3B5 gene is represented by the grey box. Translated sequences are filled with grey, and 5' and 3' untranslated regions are shown as open boxes. The +1 position corresponds to the ATG of the translation start site. (b) Genetic crosses were conducted with flies carrying the UAS-SF3B5 rescue construct or the actin5C-GAL4 driver on chromosome 2, and the sf3b5EY12579 allele on chromosome 3. Surviving adult progeny were scored for the presence of the balancer chromosomes using the curly wing phenotype (CyO) and the bristle marker stubble (MKRS). The number of surviving adult progeny and the total number of flies scored are shown for each genotype. (c) Mutant fly eyes were generated using the GMR-hid technique with the following genotypes, Ubi-nlsGFP (wild type), ada2b and sf3b5EY12579. A representative image from a single male fly of each indicated genotype is shown. (d) Mean eye widths of mutant fly eyes generated as described in panel (c) were determined for each indicated genotype. The widths of four separate fly eyes from four independent animals (one eye per animal) were measured, and standard deviation is indicated by error bars. Full genotypes of flies are shown in Supplemental Table S2.