Fig. 1.
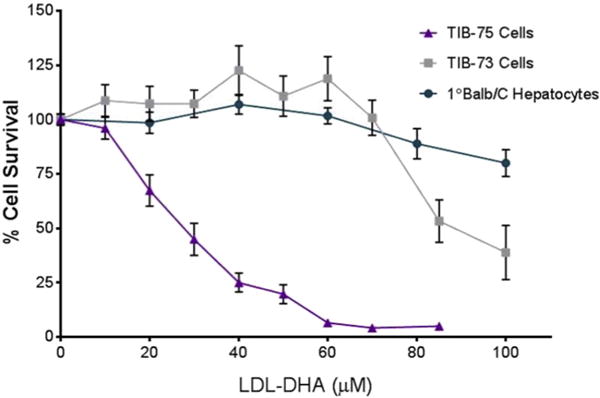
Cytotoxicity of LDL-DHA in TIB-73, TIB-75, and 1° Balb/C hepatocytes TIB-73, TIB-75, and primary Balb/C hepatocytes were treated for 72 h with increasing doses of LDL-DHA (0–200 μM DHA) after serum starvation. TIB-75 cells were more sensitive to LDL-DHA treatment (IC50 = 27.7 μM LDL-DHA) than TIB-73 cells (IC50 = 91.4 μM LDL-DHA) and Balb/C primary hepatocytes (148.8 μM LDL-DHA). The error bars represent the standard error of the mean (n ≥ 5). Viability was significantly lower from untreated cells for TIB-75 cells starting at 20 μM LDL-DHA (p-value < 0.0001), TIB-73 cells starting at 85 μM LDL-DHA (p-value < 0.0001), and primary Balb/C hepatocytes at 80 μM LDL-DHA (p-value = 0.0025) and continuing from 100 μM LDL-DHA (p-value < 0.0001).
