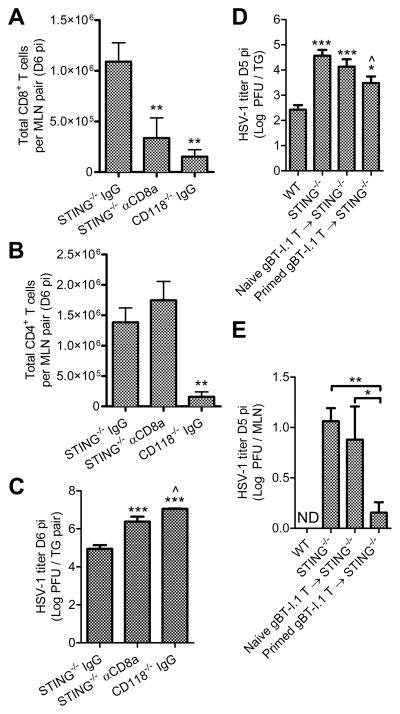
Figure 8. Augmentation of CD8+ T cells in STING−/− mice.
Antibody-mediated depletion of CD8+ T cells by administration of 200 μg anti-CD8a or IgG isotype control antibody at days 3 and 5 pi showing (A) CD8+ and (B) CD4+ T cells in the MLN at day 6 pi, (C) HSV-1 titers in the TG following CD8+ T cell depletion (n = 5–7 mice/group; 3 independent experiments). Adoptive transfer of 3×106 naive CD8+ T cells isolated from uninfected gBT-I.1 mice or primed CD8+ T cells isolated from HSV-1 infected gBT-I.1 mice and injected IV into STING−/− mice 24 hours post infection showing impact on viral titers in the (D) TG and (E) MLN at day 5 pi relative to WT controls (n = 6–12 mice per group; 3–5 independent experiments; ND, not detected). See Supplmental Fig. 1 for flow cytometry gating strategies. Stastical differences were determined by one-way ANOVA with Student-Newman-Keuls multiple comparisons tests; significance thresholds are as follows: p < 0.05 = *, p < 0.01 = **, p < 0.001 = ***; for A–C * and ^ reflect differences from STING−/− IgG and STING−/− αCD8a, respectively. In panels D–E, * and ^ reflect differences from WT and STING−/− controls, respectively, unless indicated otherwise. Bars represent mean ± SEM.