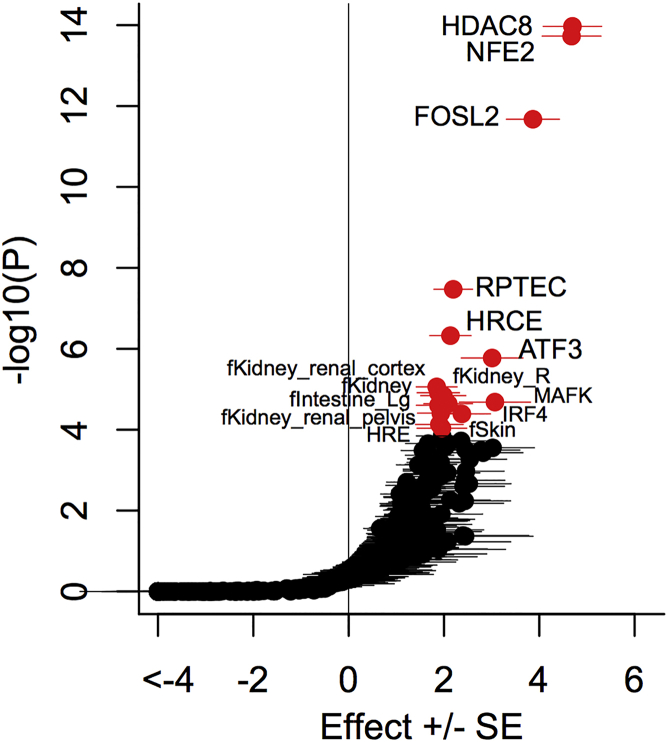
Figure 1.
DNase I Hypersensitivity Sites in Kidney Cells and HDAC8 Binding Sites are Predictive of Posterior Probability of Driving Association Signals at 20 eGFR Loci
We tested whether genomic annotations of regulatory chromatin state for 93 cell types, DNase I hypersensitivity sites (DHSs) for 145 cell types, and chromatin immuno-precipitation sequence binding sites for 165 transcription factors were predictive of posterior probability of driving eGFR association signals. Each point corresponds to an annotation, plotted according to the effect size (log-odds ratio for driving association signal) on the x axis and ranked according to the significance of the association on the y axis. Significant association (p < 0.00012, highlighted in red) was defined by Bonferroni correction for 403 tested annotations. The most significant effects included DHSs in kidney cells (RPTECs and HRCEs) and binding sites for HDAC8.