Figure 2.
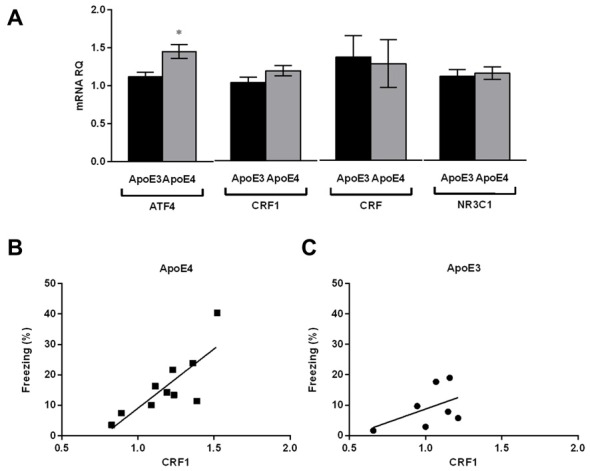
HF-ApoE4 do not express stress-induced plasticity in the amygdala compared to HF-ApoE3 mice, but display correlation between corticotropin releasing factor 1 (CRF1) expression and freezing percent post foot-shock. Whole amygdala was punched from the brains of mice maintained on a HF diet, and mRNA was extracted for evaluation of specific mental stress-related genes as well as the metabolic stress-related gene activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4). (A) There were no significant differences between HF-ApoE4 and HF-ApoE3 mice in CRF1 (t(15) = 1.554, p = 0.1411), CRF (t(15) = 0.1911, p = 0.8510), and NR3C1 (t(15) = 0.3328, p = 0.7439). ATF4 expression was higher in HF-ApoE4 (1.449 ± 0.08855, n = 10) compared to HF-ApoE3 mice (1.116 ± 0.05892, n = 7; t(15) = 2.831, *p = 0.0126). (B,C) Correlations; (B) HF-ApoE4 mice displayed significant correlation between amygdala CRF1 mRNA and foot shock-dependent freezing percent (p = 0.0052, R2 = 0.6446). (C) However, there was no significant correlation in HF-ApoE3 mice between amygdala CRF1 mRNA and freezing percent (p = 0.2656, R2 = 0.2389). Correlation was analyzed using Pearson r test. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM.
