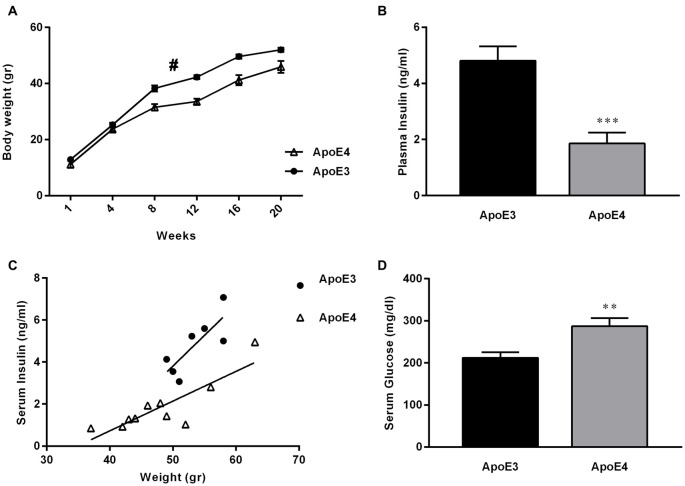
Figure 3.
ApoE4 mice develop diabetes mellitus (DM)-like metabolic features following maintenance on a HF diet. (A) ApoE4 mice gained significantly less weight over a HF diet period of 20 weeks compared to ApoE3 mice (Two-way repeated measures ANOVA, strain effect; F(1,16) = 13.54, #p = 0.0020). (B) Serum-insulin was extracted and evaluated from 24 h fasted ApoE4 mice and ApoE3 controls after a 23 week HF diet consumption. HF-ApoE4 mice showed significantly lower levels of serum insulin (1.857 ± 0.3930, n = 10), compared with HF-ApoE3 mice (4.809 ± 0.5133, n = 7; t(15) = 4.643, ***p = 0.0003). (C) Correlation between body weight and serum insulin was evaluated. There was a stronger correlation in HF-ApoE4 mice (R2 = 0.7317, **p = 0.0016), compared to HF-ApoE3 mice (R2 = 0.6297, p = 0.0332). In addition, linear regression test demonstrated significant differences between elevations or intercepts (F(1,14) = 21.7475, ***p = 0.00036), and no differences between slopes (F(1,13) = 2.65066, p = 0.1275). (D) Serum-glucose was extracted from non-fasting ApoE4 and ApoE3 mice after a 20 week HF diet. HF-ApoE4 mice showed significantly higher glucose levels (287.2 ± 19.25, n = 10) compared with HF-ApoE3 age matched controls (212.1 ± 13.25, n = 7; t(15) = 2.924, **p = 0.0105). Data are shown as the mean ± SEM. #Relates to the repeated measuring effect of body weight between the groups (p < 0.05). Correlations were analyzed using the Pearson r test.