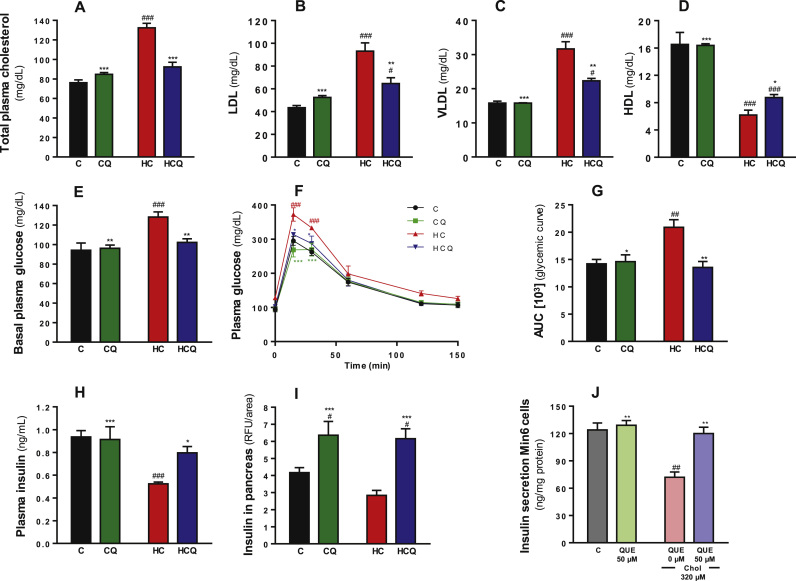
Fig. 1.
Quercetin protects against the alteration on glucose and insulin levels in plasma, and pancreatic islet insulin levels induced by a high cholesterol diet and against impairments of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in Min6 cells exposed to cholesterol. Rats were fed for 4 weeks with control diet (C), control diet containing 0.5% quercetin (CQ), high cholesterol diet (HC) or high cholesterol diet containing 0.5% quercetin (HCQ). A) Plasma glucose levels were measured after 12 h fasting. B) Results of an intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test are shown for rats fed C diet (•), CQ ( ), HC (
), HC ( ) and HCQ (
) and HCQ ( ), in which plasma glucose levels were recorded at 0, 15, 30, 60, 120 and 150 min after glucose ip. injection and C) the area under the curve (AUC) was calculated. D) Insulin levels in plasma and E) in pancreatic islets were measured after 12 h fasting. The fluorescence of the insulin was normalized to the Islet and tissue areas. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. N=6–8 rats/group. F) Insulin levels in the media of Min6 cells were determined in response to glucose (25 mM, for 1 h) after 6 h incubation with 320 µM cholesterol (Chol) and/or 50 µM QUE. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM, from three independent culture preparations, each treatment performed in quadruplicate. All two-way ANOVAs, symbols indicate Bonferroni post-test significances #relative to control diet and *to HC diet or #relative to control and *to cholesterol-treated Min6 cells.
), in which plasma glucose levels were recorded at 0, 15, 30, 60, 120 and 150 min after glucose ip. injection and C) the area under the curve (AUC) was calculated. D) Insulin levels in plasma and E) in pancreatic islets were measured after 12 h fasting. The fluorescence of the insulin was normalized to the Islet and tissue areas. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. N=6–8 rats/group. F) Insulin levels in the media of Min6 cells were determined in response to glucose (25 mM, for 1 h) after 6 h incubation with 320 µM cholesterol (Chol) and/or 50 µM QUE. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM, from three independent culture preparations, each treatment performed in quadruplicate. All two-way ANOVAs, symbols indicate Bonferroni post-test significances #relative to control diet and *to HC diet or #relative to control and *to cholesterol-treated Min6 cells.