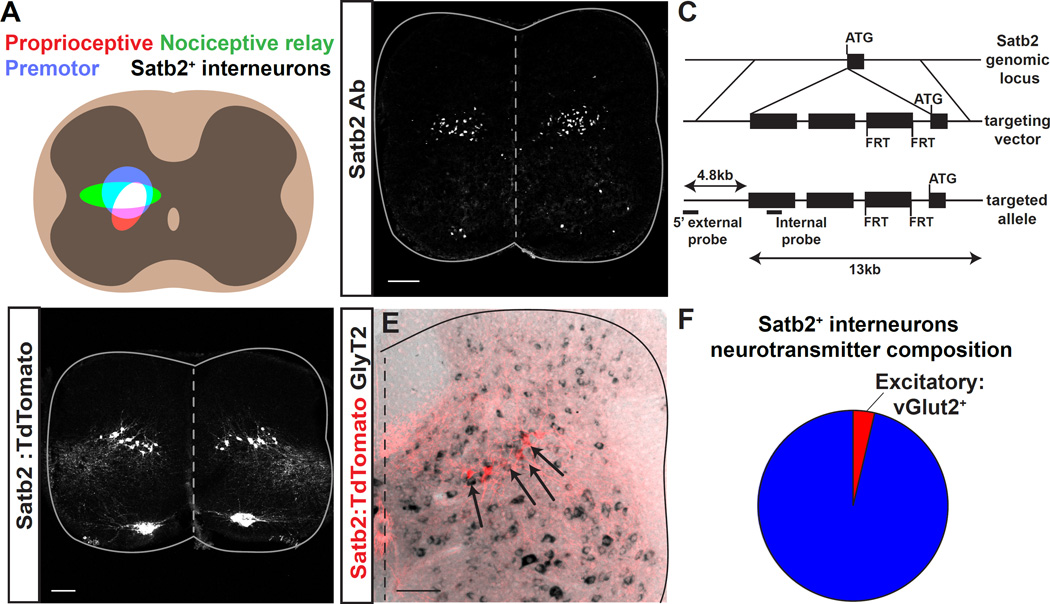
Figure 1. Expression of Satb2 in inhibitory neurons in the spinal cord deep dorsal horn.
A. Schematic illustrating the alignment of Satb2+ interneurons with the termination domains of multiple motor control pathways. Left, Premotor neurons (blue), proprioceptive fiber termination (red), and nociceptive relay neurons (green) are located in the spinal cord deep dorsal horn. The overlap between these pathways is shown in white. Right, Location of Satb2+ interneurons aligns with the overlap in left panel. B. Immunohistochemistry using a Satb2-specific antibody (Satb2 Ab) reveals Satb2 expression in a subset of motor neurons in the medial motor column (MMC) and a band of spinal interneurons at embryonic day 15.5. C. Schematic for generation of Satb2-CreERT2 mouse line. Targeted insertion of CreERT2-WPRE-pA-FRT-neo-FRT cassette into the ATG of the Satb2 locus. D. Crossing Satb2-CreERT2 with the reporter line Rosa-CAG-LSL-TdTomato (Satb2:TdTomato) recapitulates the pattern of expression seen in B. Lumbar, e18.5. See also Figure S1. E. Dorsal spinal cord following in situ hybridization for the inhibitory neurotransmitter marker GlyT2 (black) in Satb2:Tomato animals (red). Double positive neurons are indicated with arrows throughout the Satb2+ interneuron population. F. Quantification of inhibitory (blue) and excitatory (red) neurotransmitter markers from Figure 1E and Figure S1. Percentages correspond to mean values. Spinal cords were analyzed at P13 for in situ hybridization. Scale bars in B, D and E, 100um.