Figure 8.
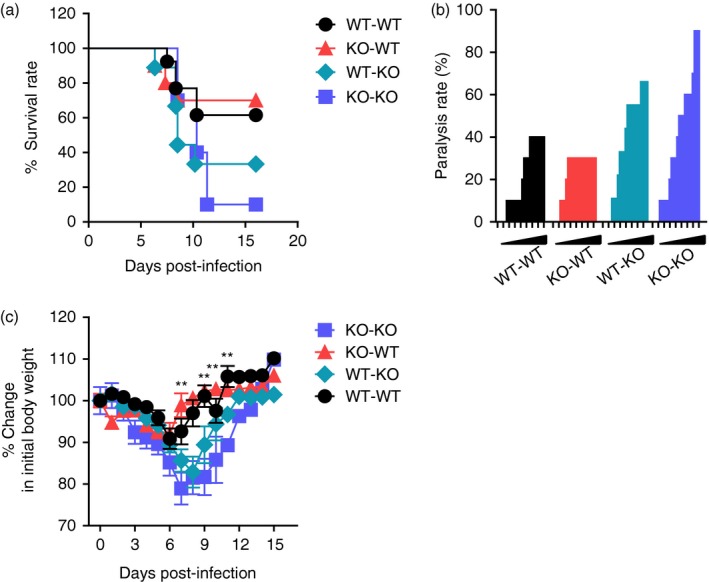
CCL2 produced from resident central nervous system (CNS) cells alleviates Japanese encephalitis (JE) progression. Bone marrow (BM) cells from wild‐type (WT) or CCL2 knockout (KO) mice were grafted to lethally irradiated WT or CCL2 KO recipient mice, which were intradermally infected with Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV; 5·0 × 107 pfu) via footpad route. (a) Susceptibility of CCL2 KO BM chimeric models to JE. Infected recipient mice (n = 10–11) were examined daily up to 16 days post‐infection (dpi) to record survival rate. (b) Ratio of mice showing neurological disorder during JE progression. CCL2 KO BM chimeric models infected with JEV were examined every 6 hr from 4 to 11 dpi, and ratio of inoculated mice showing neurological disorder was recorded. (c) Change in body weight. Data are expressed as the mean percentage ± SD of body weight relative to time of challenge. *P < 0·05; **P < 0·01; ***P < 0·001 compared between KO‐WT and WT‐KO BM chimeric model.
