Figure 6.
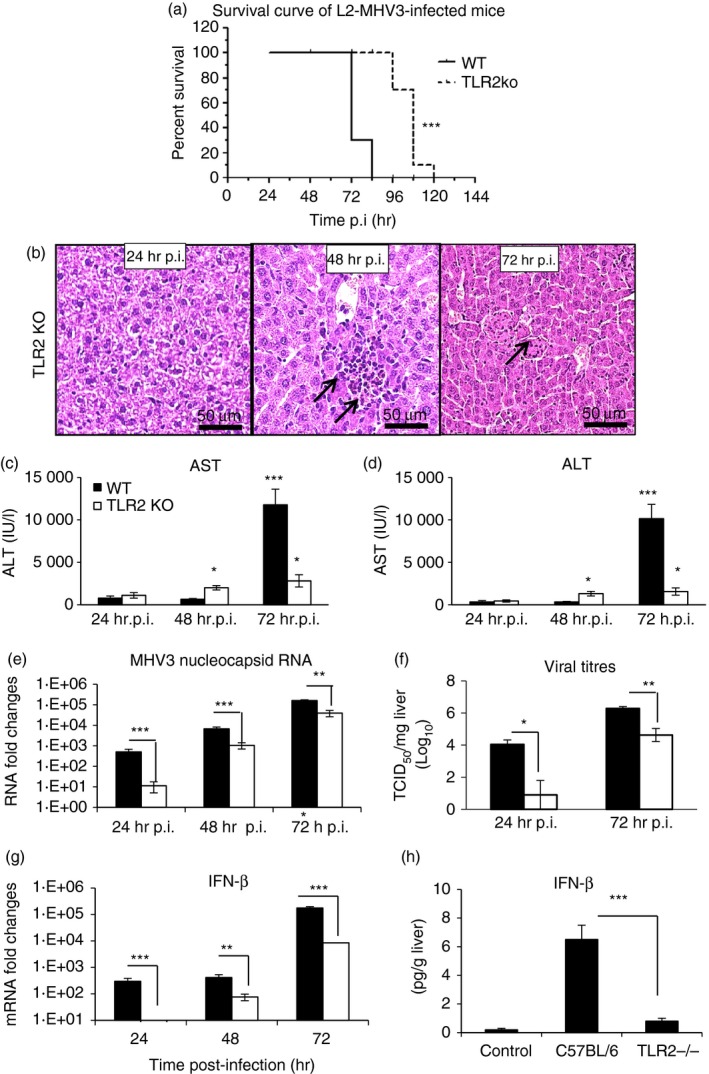
Hepatic damages, viral replication and interferon‐β (IFN‐β) production in the liver of murine hepatitis virus (MHV) 3‐infected wild‐type (WT) and Toll‐like receptor 2 knockout (TLR2 KO) mice. Groups of six to seven C57BL/6 (WT) and TLR2 KO mice were intraperitoneally (i.p.) infected with 1000 TCID50 of MHV3. Survival curve of MHV3‐infected WT and TLR2 KO mice (a). Histopathological analysis was conducted on livers from MHV3‐infected TLR2 KO at 24, 48 and 72 hr post‐infection (p.i.) (b). Serum samples from MHV3‐infected WT and TLR2 KO mice were assayed for aspartate transaminase (AST) (c) and alanine transaminase (ALT) (d) activity at 24–72 hr p.i. Replication of MHV3 in livers of infected mice was determined by analysis of the nucleoprotein (MHV‐N) RNA expression at 24, 48 and 72 hr p.i. by quantitative RT‐PCR, and by viral titration (TCID50) at 24 and 72 hr p.i. (e, f). Messenger RNA fold increases for IFN‐β were analysed in livers from MHV3‐infected mice by quantitative RT‐PCR at 24, 48 and 72 hr p.i. (g). Values represent fold change in gene expression relative to mock‐infected mice (arbitrary value of 1) after normalization with HPRT expression. Protein levels of IFN‐β in the liver were quantified by ELISA test at 72 hr p.i. (h). (*P < 0·05; **P < 0·01; ***P < 0·001).
