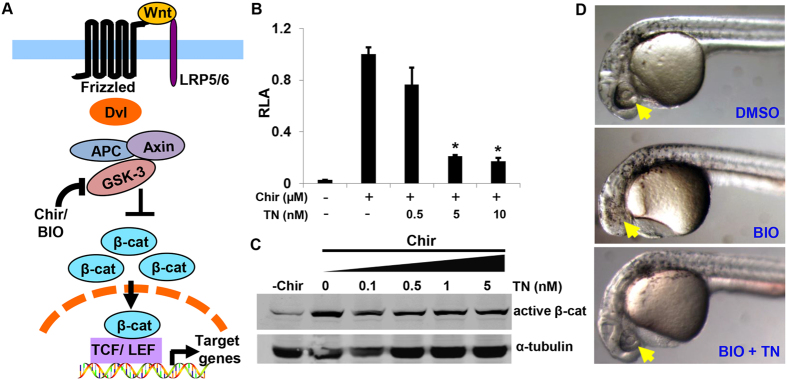
Figure 2. Triptonide may inhibit Wnt/β-catenin signaling downstream of GSK-3β, a key component of the β-catenin destruction complex.
(A) Cartoon model illustrates Wnt/β-catenin signaling with various means to modulate the pathway. Briefly, disruption of the β-catenin degradation complex, through pharmacological inhibition of GSK-3β using the small molecule CHIR 99021 (Chir) or BIO, leads to nuclear β-catenin accumulation and subsequent Wnt reporter activation. (B) Triptonide blocked Wnt/β-catenin signaling induced by GSK-3β antagonist Chir (2 μM) in a dose dependent manner. Results of luciferase assay were represented as mean relative luciferase activities (RLA) + SEM (n = 3). All the P values are compared to the luciferase activity induced by Chir (*P < 0.05). (C) Triptonide did not regulate active β-catenin expression levels. (D) Triptonide reproducibly rescued the loss of eyes in in BIO-induced zebrafish embryos. Embryos were exposed to DMSO or 100 nM triptonide in the presence of 0.3 μM BIO at the shield stage (6 hpf) and the images were taken at 30 hpf. 15 embryos treated with 0.3 μM BIO resulted in 14 fish with double eye loss in the control, and 15 embryos treated with both 100 nM triptonide and 0.3 μM BIO led to 13 fish with appearance of both eyes at 30 hpf (P < 0.0001). P-value was calculated with GraphPad Prism V6.