Fig. 3.
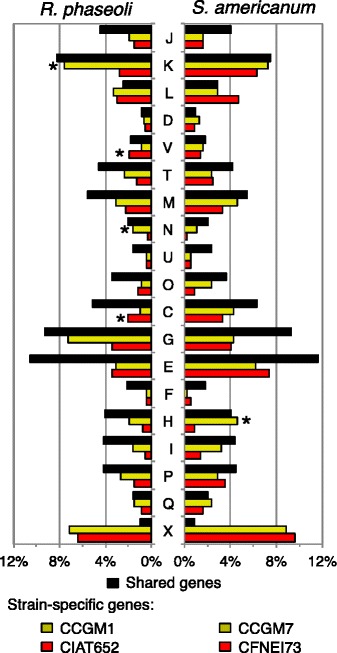
Functional classification of orthologs and strain-specific genes. Left, Rhizobium phaseoli. Right, Sinorhizobium americanum. Yellow, seed-borne strain. Red, nodule strain. Black, orthologs between the pair of strains. Distribution by COG functional categories. Letters: J Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis, K Transcription, L Replication, recombination and repair, D Cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning, V Defense mechanisms, T Signal transduction mechanisms, M Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis, N Cell motility, U Intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport, O Post-translational modification, protein turnover, and chaperones, C Energy production and conversion, G Carbohydrate transport and metabolism, E Amino acid transport and metabolism, F Nucleotide transport and metabolism, H Coenzyme transport and metabolism, I Lipid transport and metabolism, P Inorganic ion transport and metabolism, Q Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport, and catabolism, and X mobile elements. Genes with general function (R), poorly characterized (S) and not in COGs (−), were not included. Asterisks denote significant difference between seed-borne and nodule strains, with p > 0.05
