Fig. 2. Detection of non-polpoid adenoma.
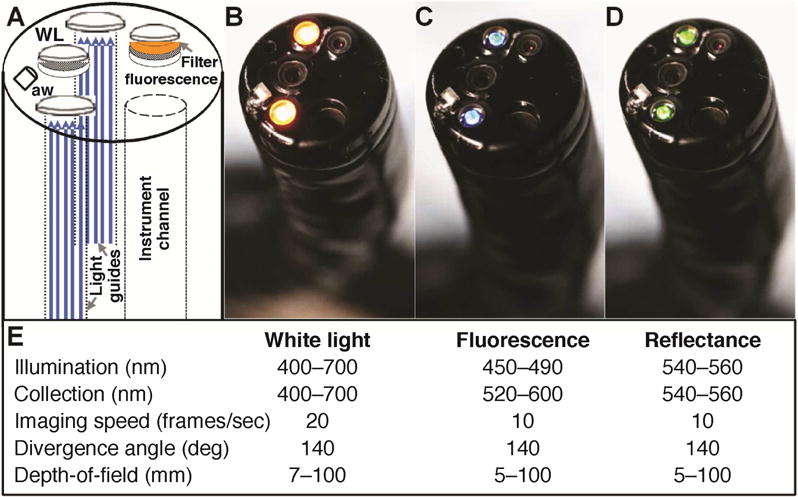
A) A cap is placed on the distal end of the multi-modal video colonoscope to flatten mucosal folds for improved visualization. On white light, a non-polypoid lesion (arrow) is seen in the proximal colon that could easily be missed. B) After topical peptide administration, the lesion is clearly visualized with fluorescence. Normal colon shows minimal background. C, D) The registered reflectance image was used to produce a ratio-image, shown in pseudo-color, that corrects for distance and geometry. Intensities can be quantified to outline the extent of the lesion (dashed red line) and guide resection.
