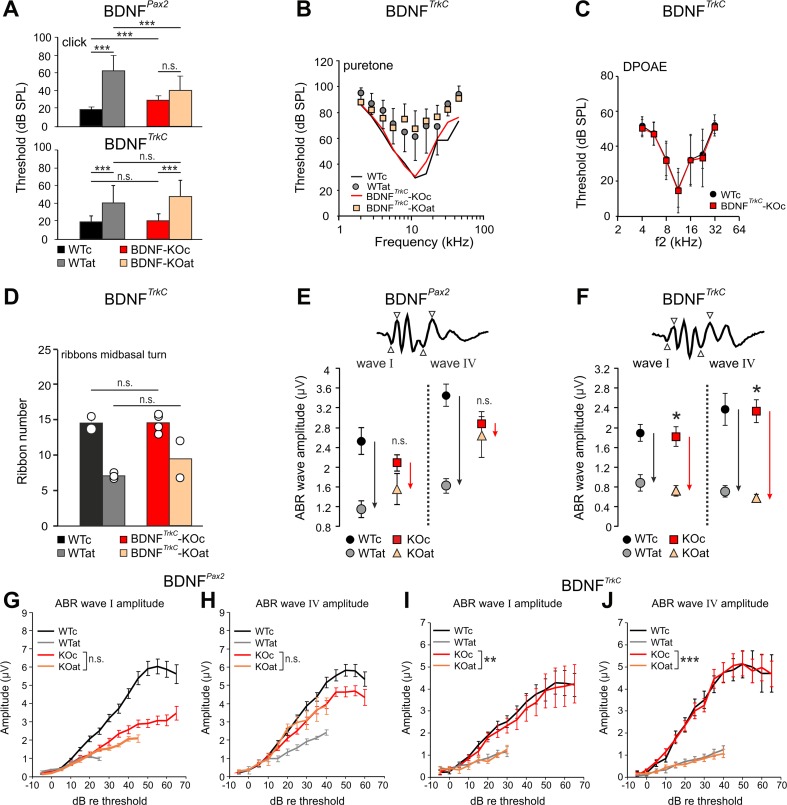
Fig. 3.
Hearing function of BDNFPax2-KO and BDNFTrkC-KO mice before and after acoustic trauma. Auditory thresholds of BDNFPax2-KO (a, upper panel) and BDNFTrkC-KO (a, lower panel) mice analyzed by click (a) and tone-burst-evoked ABR (b) before (KOc) and after acoustic trauma (KOat). Compared to WT mice (WTc, WTat), BDNFPax2-KO are less vulnerable [25]. BDNFTrkC-KO mice exhibited normal hearing thresholds (a, lower panel, WTc, ears/mice: n = 22/11; KOc, n = 20/10; p > 0.999, two-way ANOVA) and show no significant difference to WT mice after acoustic trauma (WTat, ears/mice: n = 8/8; KOat, n = 7/7; p = 0.543, two-way ANOVA). Error bars, SD. c DPOAE thresholds in BDNFTrkC-WT and BDNFTrkC-KO mice were similar (WT, ears/mice: n = 19/10; KOn = 20/10; p = 0.482, two-way ANOVA). Error bars, SD. d IHC ribbon counts of midbasal cochlear turns in BDNFTrkC-WT and BDNFTrkC -KO mice before (WTc, KOc) and after noise exposure (WTat, KOat). The ribbon number of BDNFTrkC-KO mice was not significantly different from that of BDNFTrkC-WT animals. Error bars, SEM, n.s. p > 0.05; WTc, sections/mice: n = 5/2; WTat, n = 6/3; KOc, n = 11/4; KOat, n = 7/2. e, f Comparison of click-evoked ABR wave amplitudes in BDNFPax2-WT and BDNFPax2-KO mice (e) and BDNFTrkC-WT (WTc, WTat) and BDNFTrkC-KO (KOc, KOat) mice (f) before (WTc, KOc) and after noise exposure (WTat, KOat). In BDNFPax2-KO, suprathreshold amplitudes of wave I (auditory nerve) and wave IV (IC) are less reduced after noise exposure than in BDNFPax2-WT mice (compare black and red arrows in e for different reductions in WT and KO, respectively). In BDNFTrkC-KO, the reduction was not different from the reduction in BDNFTrkC-WT mice (compare black and red arrows in f for similar reduction in WT and KO, respectively). Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test (e) wave I, n.s. p = 0.254; wave IV, n.s. p = 0.893; WTat, ears/mice: n = 8/4; KOat, n = 7/4; f wave I, *p = 0.04; wave IV, *p = 0.02; WTat, mice/ears: n = 8/16; KOat, n = 8/16; error bars, SEM. g–j Suprathreshold ABR amplitude at the level of the auditory nerve (wave I) and IC (wave IV). Analysis was performed before and after acoustic trauma in BDNFPax2-WT (WTc, n = 16/8 ears/mice; WTat, n = 16/8 ears/mice) and BDNFPax2-KO mice (KOc, n = 16/8 ears/mice; KOat, n = 16/8 ears/mice) (g, h) compared to BDNFTrkC-WT (WTc, n = 17/8 ears/mice; WTat, n = 8/4 ears/mice) and BDNFTrkC-KO mice (KOc, n = 15/8 ears/mice; KOat, n = 7/4 ears/mice) (i, j). Note the near-complete convergence of growth functions of ABR wave I (g, n.s. p = 0.275; i, **p = 0.008) and IV (h, n.s. p = 0.420; j, ***p < 0.001) before and after AT in BDNFPax2-KO but not in BDNFTrkC-KO mice. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test, error bars, SEM