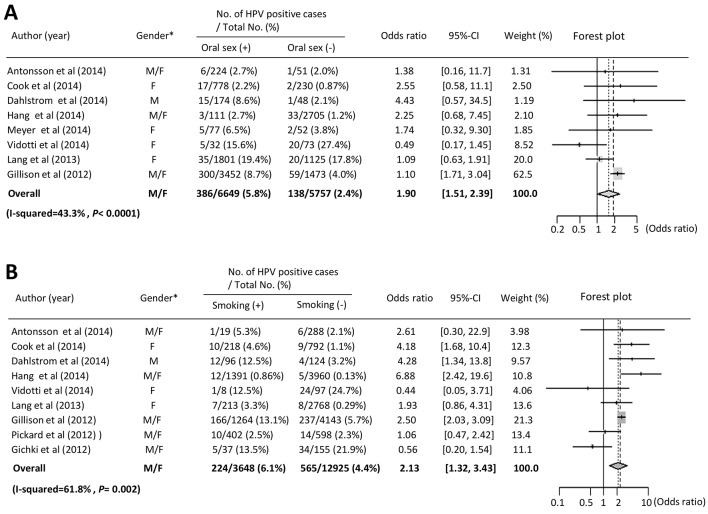
Figure 2.
Meta-analysis of the association between oral HPV infection and sexual behavior, smoking and drinking. (A) Forest plot of overall oral HPV infection and oral sex. Meta-analysis using a fixed effects model demonstrated that oral sex was significantly correlated with oral HPV infection (P < 0.0001). *Gender: M: male; F: female. (B) Forest plot of overall HPV infection and smoking. Meta-analysis using a random effects model demonstrated that smoking status was significantly correlated with oral HPV infection (P = 0.002). *Gender: M: male; F: female.