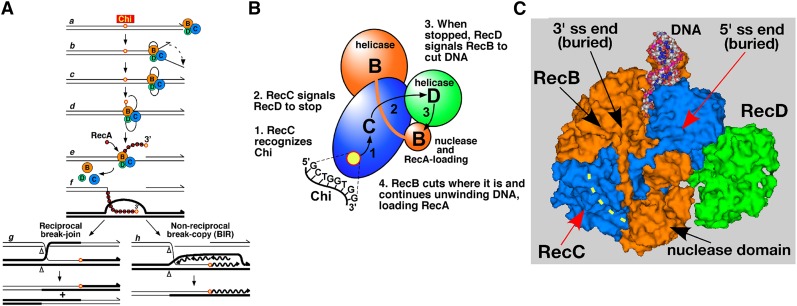
Figure 1.
Models for recombination and regulation of RecBCD enzyme by Chi hotspots, and RecBCD structural features involved in its context-dependent response to Chi. See text for further explanations. (A) Model for RecBCD-promoted recombination (Amundsen et al. 2007). Break-induced replication (BIR). (B) Intersubunit signal transduction model for regulation of RecBCD enzyme activities in response to Chi (Amundsen et al. 2007). (C) The RecBCD-ds DNA complex shown in a surface representation (PDB 1W36; Singleton et al. 2004). The RecB, C, and D subunits are colored as in panels A and B. The bound DNA has four terminal unwound bp; the 3′ terminus extends into the RecB helicase domain and the 5′ terminus extends into RecC headed toward the RecD helicase domain. Dotted yellow line represents the RecC tunnel in which Chi is putatively recognized. See Figure 2 for additional views.