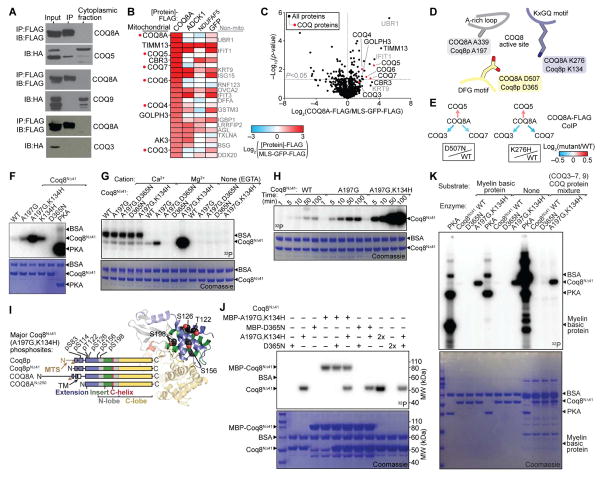
Figure 3. COQ8A Interacts with Complex Q but Lacks Protein Kinase Activity in trans.
(A) Immunoblot (IB) analysis of interactions between COQ8A-FLAG and COQ5-HA, COQ3-HA, or COQ9-HA transfected into COS cells and immunoprecipitated (IP’d) using anti-FLAG beads.
(B) Heatmap showing the top 25 endogenous proteins most enriched by COQ8A-FLAG IP’d from HEK293 cells compared to various control IPs (mean, n = 4).
(C) Relative abundances of endogenous proteins co-purifying with COQ8A-FLAG compared to MLS-GFP-FLAG (mean, n = 4) IP’d from HEK293 cells as assessed by LC-MS/MS.
(D) Cartoon of COQ8 active site residues (based on PDB 4PED).
(E) Relative abundances of endogenous COQ proteins co-purifying with COQ8A-FLAG (log2(mutant/WT)) IP’d from HEK293 cells as assessed by LC-MS/MS.
(F) SDS-PAGE analysis of in vitro Mg[γ-32P]ATP autophosphorylation reactions with Coq8NΔ41 variants or PKA. BSA, bovine serum albumin (reaction buffer component).
(G) Divalent cation dependence of Coq8NΔ41 autophosphorylation.
(H) Time course of Coq8NΔ41 autophosphorylation.
(I) Coq8NΔ41 autophosphorylation sites identified by LC-MS/MS mapped onto a homology model of Coq8p (based on COQ8A structure, PDB 4PED).
(J) SDS-PAGE analysis of in vitro Mg[γ-32P]ATP autophosphorylation reactions with combinations of Coq8NΔ41 variants. MBP, maltose binding protein tag.
(K) SDS-PAGE analysis of in vitro Mg[γ-32P]ATP kinase reactions with PKA or Coq8NΔ41 and potential substrate proteins.
See also Figure S3.