Figure 3. Expression and structural characteristics of WAP domain–containing proteins of T. muris.
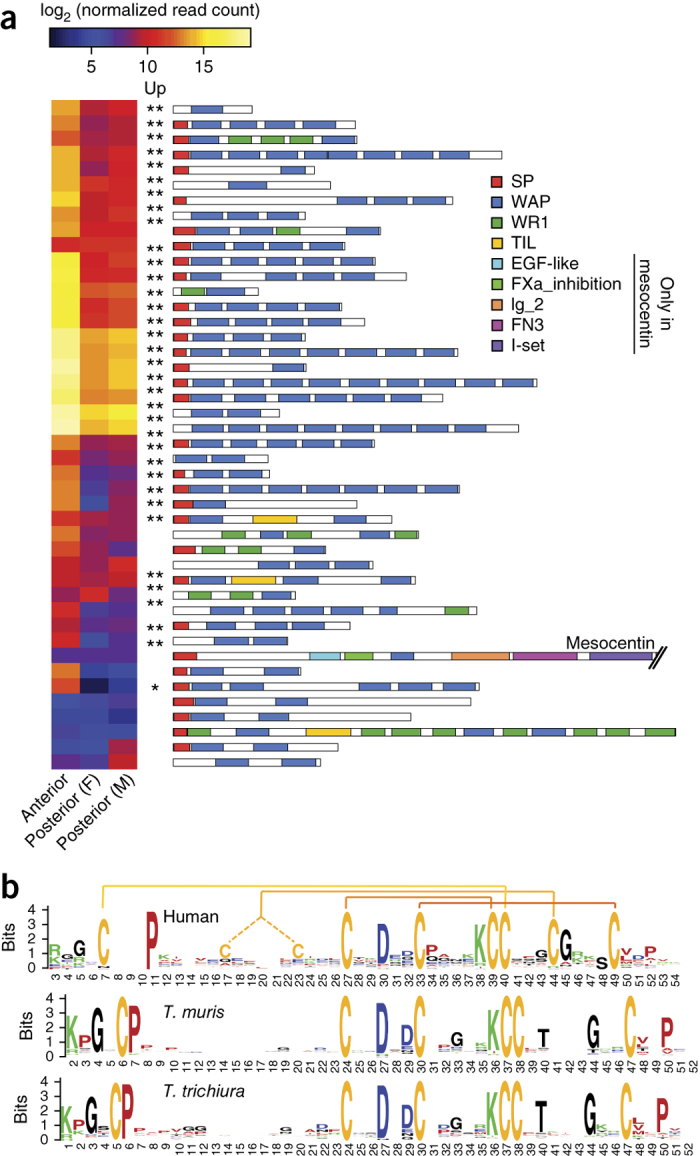
(a) Normalized transcript levels of the 44 genes encoding WAP domain–containing proteins in T. muris, comparing the parasite anterior region with the posterior regions of adult female (F) and male (M) parasites. Indication of significant transcriptional upregulation in a particular pairwise comparison (Up) refers to false discovery rate (FDR) % 0.01 and FDR % 1 × 10−5 when denoted by one asterisk and to FDR % 1 × 10−5 when denoted by two asterisks. SP, signal peptide; WAP, whey acidic protein (Interpro, IPR008197); WR1, cysteine-rich repeat (IPR006150); TIL, trypsin inhibitor–like (IPR002919). For a full version of this figure, see Supplementary Figure 4a. (b) Sequence logos show the conserved and distinct sequence characteristics of the WAP domains (Interpro, IPR008197) found in proteins from H. sapiens, T. trichiura and T. muris. The four canonical disulfide bonds formed by eight cysteine residues are highlighted at the top of the sequence logo for human WAP domains. The sequence logos representing the different species are aligned around the central CXXDXXC motif (where X is any amino acid). For a full version of this figure, see Supplementary Figure 5.
