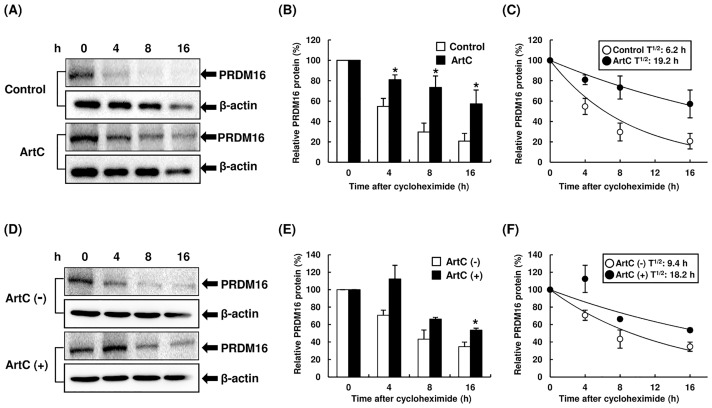
Fig 4. The degradation of PRDM16 protein levels in C3H10T1/2 cells treated with vehicle or ArtC.
(A, B) The degradation of PRDM16 protein in C3H10T1/2 cells differentiated with or without ArtC. C3H10T1/2 cells were differentiated with or without ArtC for 8 days, and then cells were treated with cycloheximide and the degradation of PRDM16 protein was examined using immunoblot analysis at the indicated time point. (C) PRDM16 protein stability over time, plotted from data in panel (B). (D, E) The degradation of PRDM16 protein in C3H10T1/2 cells differentiated without ArtC. C3H10T1/2 cells were differentiated without ArtC for 8 days, then the cells were treated with vehicle or ArtC in medium containing cycloheximide. The degradation of PRDM16 protein was examined using immunoblot analysis at the indicated time point. (F) PRDM16 protein stability over time, plotted from data in panel (E). (B, E) The data are presented as means ± SEM (n = 3–5); * mean values are significantly different from those of the control (B) or ArtC (-) (E) at P < 0.05 (Student’s t-test).