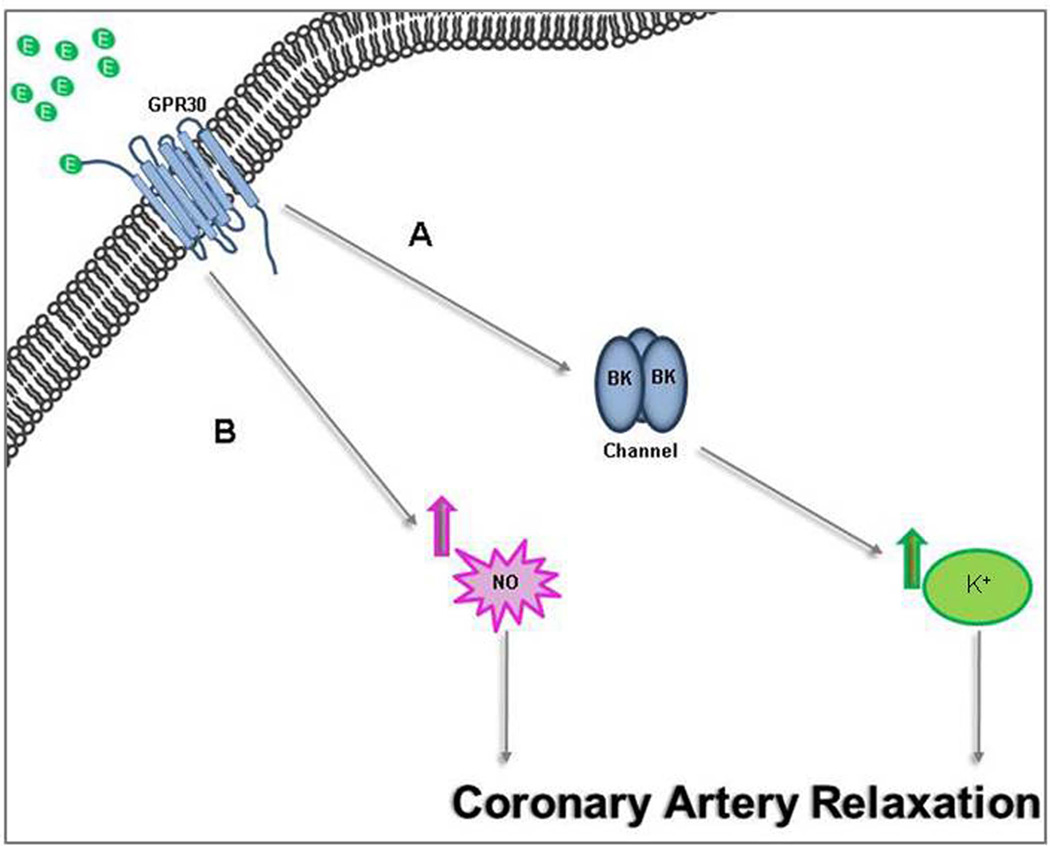
Figure 4. GRP30 activation via endothelium-independent or endothelium-dependent mechanisms.
A: Endothelium-independent effect is mediated by a large conductance calcium-activated potassium channel leading to an increase in potassium efflux. This effect results in coronary artery relaxation. BK, Ca2+- and voltage-activated K+ channels. B: Endothelium-dependent mechanism. Estrogen binding to GPR30 leads to activation of eNOS raising the production of nitric oxide (NO) in coronary endothelial cells to relax these arteries.