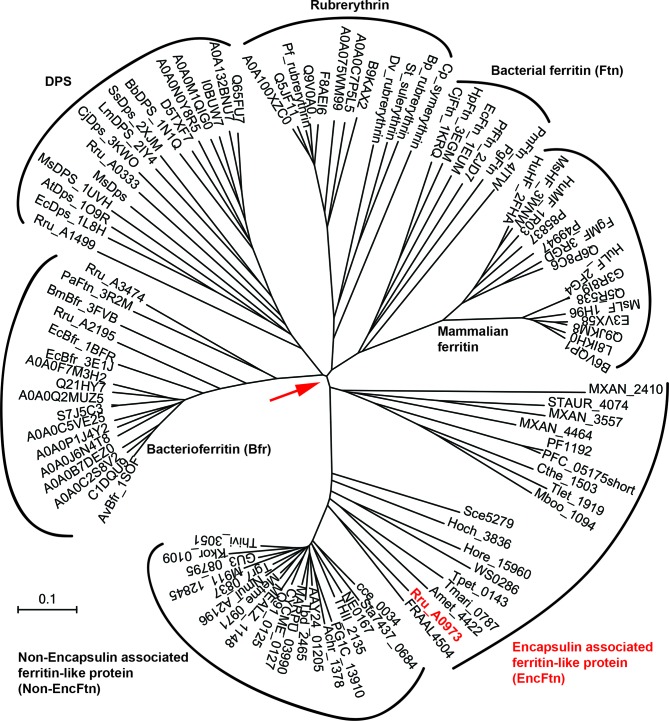
Figure 13. Phylogenetic tree of ferritin family proteins.
The tree was built using the Neighbor-Joining method (Saitou and Nei, 1987) based on step-wise amino acid sequence alignment of the four-helical bundle portions of ferritin family proteins (Supplementary file 1). The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree; the likely root of the tree is indicated by a red arrow. The evolutionary distances were computed using the p-distance method (Nei and Kumar, 2000) and are in the units of the number of amino acid differences per site. The rate variation among sites was modeled with a gamma distribution (shape parameter = 2.5). The analysis involved 104 amino acid sequences. All ambiguous positions were removed for each sequence pair. There were a total of 262 positions in the final dataset. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA7 (McCoy et al., 2007)