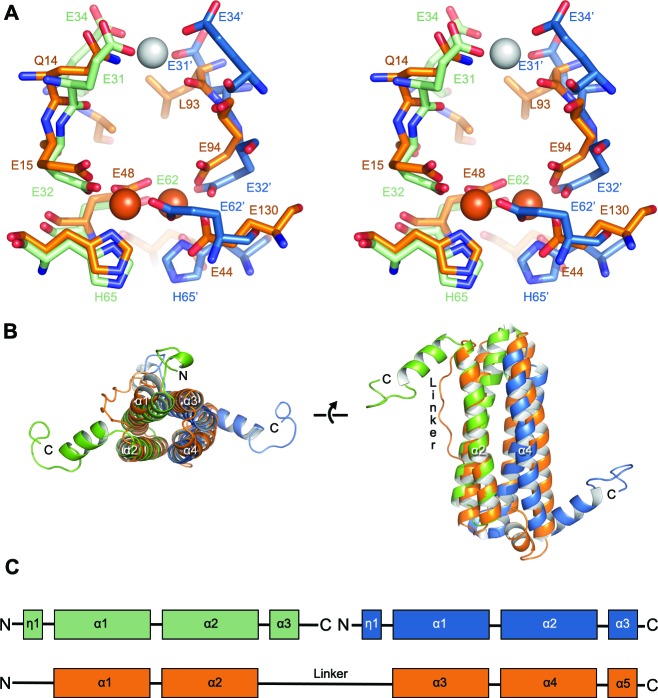
Figure 6. Comparison of the symmetric metal ion binding site of EncFtnsH and the ferritin FOC.
(A) Structural alignment of the FOC residues in a dimer of EncFtnsH (green/blue) with a monomer of Pseudo-nitzschia multiseries ferritin (PmFtn) (PDBID: 4ITW) (orange) (Pfaffen et al., 2013). Iron ions are shown as orange spheres and a single calcium ion as a grey sphere. Residues within the FOC are conserved between EncFtn and ferritin PmFtn, with the exception of residues in the position equivalent to H65’ in the second subunit in the dimer (blue). The site in EncFtn with bound calcium is not present in other family members. (B) Secondary structure of aligned dimeric EncFtnsH and monomeric ferritin highlighting the conserved four-helix bundle. EncFtnsH monomers are shown in green and blue and aligned PmFtn monomer in orange as in A. (C) Cartoon of secondary structure elements in EncFtn dimer and ferritin. In the dimer of EncFtn that forms the FOC, the C-terminus of the first monomer (green) and N-terminus of the second monomer (blue) correspond to the position of the long linker between α2 and α3 in ferritin PmFtn.