Fig. 2.
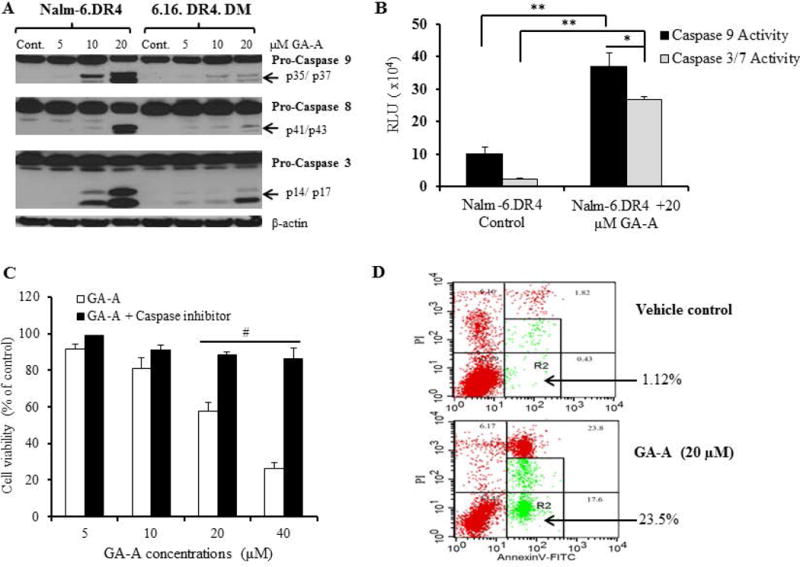
GA-A induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in B-cell lymphoma. (A) Western blot analysis showing protein expression and cleavage of active caspases 9, 8, and 3 in cells treated with GA-A (5–20µM) or vehicle alone (control) as described in the methods. β-actin was utilized as a loading control. (B) Caspase activity was measured in cells treated with GA-A (20μM) or vehicle alone for 24h at 37°C in 96-well plate as described. The plate was equilibrated to 22°C, followed by the addition of Caspase-Glo® 9 or Caspase-Glo® 3/7 reagents as per manufacturer recommendations. Luminescence was recorded at 30 min after adding the reagent. (C) Inhibition of caspases by a pan caspase inhibitor (Z-VAD-FMK) blocked GA-A-induced anti-proliferative activity in NALM-6.DR4 pre-B acute lymphocytic leukemia cells. Cells were treated with GA-A (5, 10, 20 and 40μM) or vehicle alone and incubated with or without Z-VAD-FMK for 24h at 37°C, followed by the MTS viability assay and calculation of anti-proliferative responses as described in the methods. The data shown are representative of at least three separate experiments. Error bars represent mean ± S.D. (D) Contour diagrams of annexin V-FITC/PI flow cytometry of NALM-6.DR4 cells after 20μM of GA-A treatment for 24h. Dot plot of forward and side scatter (20,000 events/sample, left panels), and annexin V/PI double staining (right panels) were shown. The R2 quadrants represent the annexin V-positive early and late apoptotic cells. The figures shown are representatives of at least three independent experiments with similar patterns, and error bars represent average ± S.D. Significant differences were calculated by student’s t test; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, #p<0.001.
