Figure 3. Calcium regulates mitochondrial dynamics and transport.
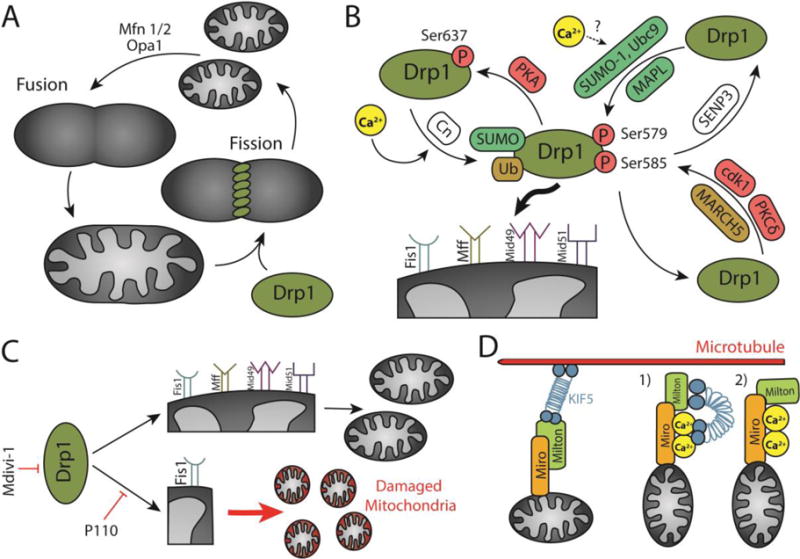
A) Mitochondrial fission/fusion cycle. Mitochondrial fusion is mediated by the outer mitochondrial membrane GTPases Mfn1 and Mfn2, and the inner mitochondrial membrane GTPase Opa1. Mitochondrial fission is regulated by the cytosolic GTPase Drp1 that anchors on the outer mitochondrial membrane. B) Post-translational modifications of Drp1 determine its localization in the cytosol or the mitochondrial membrane. PKA, cdk1, and PKCδ phosphorylate Drp1. Calcineurin (Cn) dephosphorylates Drp1. SUMO-1, Ubc9, and MAPL SUMOylate Drp1. SENP3 deSUMOylates Drp1. MARCH 5 ubiquitinates Drp1. Calcium is an activator of calcineurin and potentially Ubc9, thus promoting Drp1 translocation to the mitochondria. Drp1 is anchored to the mitochondrial membrane through four adaptors: Fis1, Mff, Mid49, and Mid51. C) Drp1 drives both physiological fission and Fis1-dependent pathological fission. While mdivi-1 is a general inhibitor of Drp1, P110 selectively inhibits pathological fission. D) Mitochondria traverse microtubules through motor adaptor complexes including Miro, Milton, and KIF5. Calcium detaches mitochondria from microtubules through two potential mechanisms: 1) KIF1 detachment from microtubules and attachment to calcium-bound Miro, and 2) Milton detachment from KIF5 and attachment to calcium-bound Miro.
