Fig. 3.
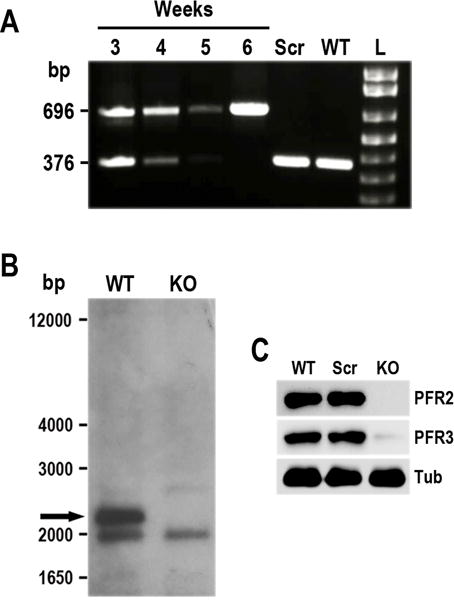
Phenotypic analysis of PFR2-KO cell line in T. cruzi. A. Time course PCR analysis of TcPFR2-KO epimastigotes at weeks 3–6 post-transfection. Disruption of the TcPFR2 gene was verified by PCR with primers annealing outside the homology regions on the blasticidin cassette (Lander et al., 2015). A fragment of 696 bp was amplified from gDNA isolated from the TcPFR2-KO mutant, indicating disruption of the PFR2 gene. The same primer set generates a fragment of 376 bp in the original locus. Notice that the band corresponding to the intact locus (376 bp) disappears with time, being undetectable at 5 weeks post-transfection. Epimastigotes expressing Cas9 and a scrambled sgRNA (Scr), and wild type (WT) epimastigotes were included in the analysis as control cell lines. L, 1 kb plus ladder (Invitrogen). B. Southern blot analysis of wild type (WT) and TcPFR2-KO (KO) epimastigotes. gDNA was digested with StuI/XhoI restriction enzymes and then used for Southern blot analysis using a 500-bp TcPFR2 probe. The band corresponding to TcPFR2 (pointed out with black arrow) is present in WT parasites and absent in KO epimastigotes. Molecular weights (bp) are shown on the left side. C. Western blot analysis of control and TcPFR2-KO epimastigotes. Total lysates (20 μg/lane) of wild-type (WT), scrambled control (Scr), and TcPFR2-KO epimastigotes (KO) were analyzed by Western blot with polyclonal antibodies anti T. cruzi PFR2 and PFR3 (Egui et al., 2012). Anti-β-tubulin antibody (Tub) was used as loading control.
