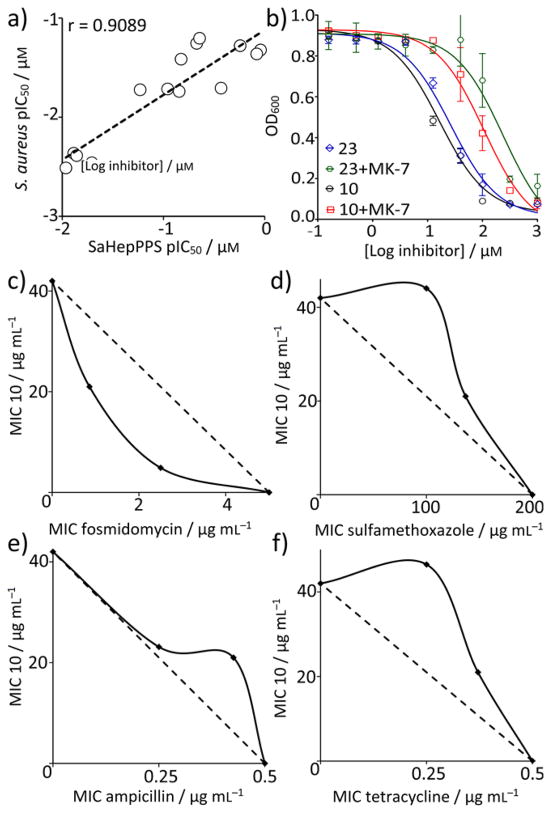
Figure 7.
Identification of targets of bisphosphonates inhibiting S. aureus cell growth. a) Correlation between S. aureus cell growth inhibition and SaHepPPS inhibition based on pIC50 (= −log10IC50 [μM]) results. b) Addition of 200 μM menaquinone-7 (MK-7) to the growth medium increases the IC50 of 10 and 23 for cell growth inhibition by a factor of ~8. Data points are shown as mean±SD, for duplicate experiments. c) 10+fosmidomycin in B. subtilis showing synergy (FICI=0.27) of 10 with a cell wall biosynthesis inhibitor (that targets DXR, 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase, in the non-mevalonate pathway). d) 10+sulfamethoxazole in B. subtilis showing an indifferent effect (FICI=1.73) of 10 with a nucleic acid biosynthesis inhibitor (that targets dihydropteroate synthase). e) 10+ampicillin in S. aureus showing an indifferent effect (FICI=1.40) of 10 and a cell wall biosynthesis inhibitor (that targets transpeptidase). f) 10+tetracycline in S. aureus showing an indifferent effect (FICI=1.85) of 10 with a protein synthesis inhibitor (that targets ribosome function).