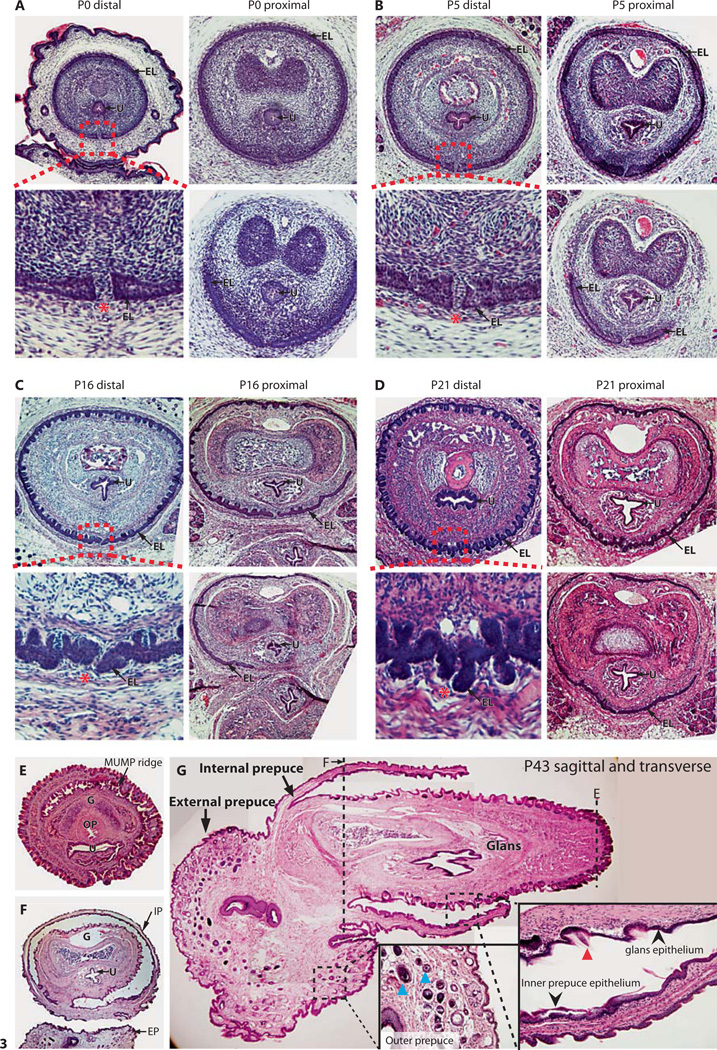
Fig. 3.
A–D Hematoxylin- and eosin-stained transverse sections of the internalized mouse penis as it develops postnatally. Red-dotted boxes indicate the terminus of the internal preputial epithelial lamina (EL), and show the site of fusion of the G and EP. Red asterisks indicate the site of preputial attachment. E, F Transverse hematoxylin- and eosin-stained sections of an adult (P47) penis in the externalized state. E Distal section showing the G, MUMP ridge, urethra (U), and os penis (OP), whereas F is more proximal and shows the IP surrounding the G and the EP. G Sagittal section of an adult (P47) mouse penis partially externalized. Red arrowhead indicates penile spines of the G, black arrowheads show the smooth mucosal epithelium of the IP, and blue arrowheads show hair follicles of the EP. Dashed lines indicate corresponding plane of transverse sections shown in E and F. For further abbreviations, see figures 1 and 2.