Figure 5.
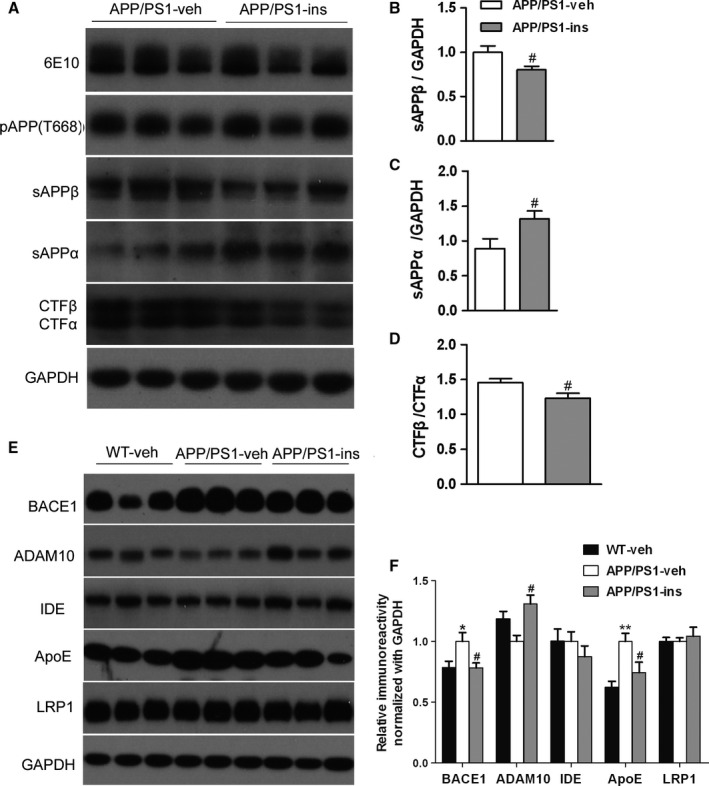
Intranasal insulin treatment alters amyloid precursor protein (APP) processing and regulates aberrant expression of BACE1, ADAM10, and Apolipoprotein E in APP/PS1 mice. (A) Representative Western blots of full‐length APP (6E10), phosphorylated APP (pT668), sAPPβ, sAPPα, and APP C‐terminal fragments (CTFα, CTFβ) in the hippocampal homogenates from APP/PS1 mice treated with insulin or vehicle. (B, C) The blots were quantified densitometrically, and the data were normalized with the GAPDH level. (D) The ratio of CTFβ to CTFα in insulin‐ or vehicle‐treated APP/PS1 mice is shown. All values are presented as mean ± SEM. # P < 0.05 vs. APP/PS1‐veh group. APP/PS1‐veh, n = 14; APP/PS1‐ins, n = 13, Student's t‐test. (E) Representative Western blots of BACE1, ADAM10, insulin‐degrading enzyme (IDE), Apolipoprotein E, LRP1, and GAPDH in the hippocampal homogenates. (F) Densitometric analysis of Western blots normalized to GAPDH, with the levels of the APP/PS1‐veh group set as 100%. Data represent mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 vs. WT‐veh group; **P < 0.01 vs. WT‐veh group; # P < 0.05 vs. APP/PS1‐veh group. n = 11 per group, one‐way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni's post hoc test.
