Figure 3.
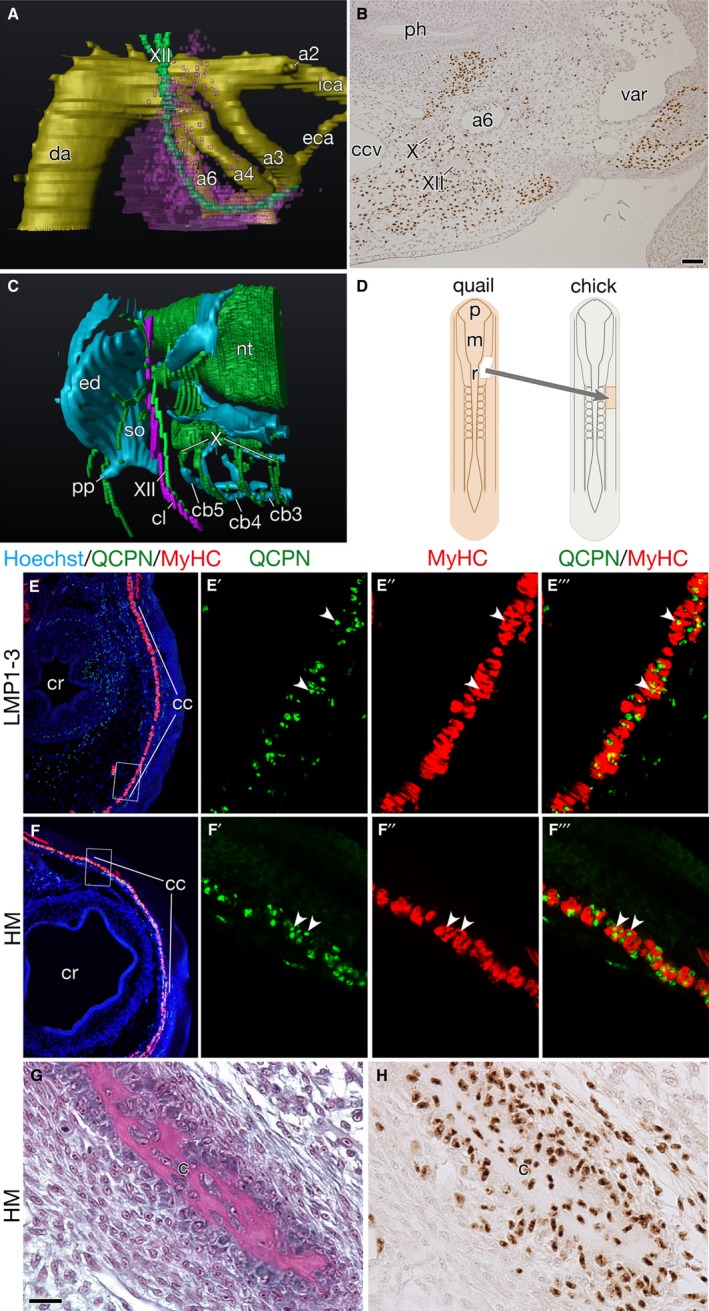
Developmental characteristics of the clavicle‐forming mesoderm. (A,B) Distribution of cells derived from LPM adjacent to somites 1–3 at HH stage 24. (A) Three‐dimensional reconstruction of the chick–quail chimera showing the distribution of quail cells (pink) around the pharyngeal arch arteries (a2–a6). (B) Horizontal section of the chimera immunostained with QCPN antibody. Note that quail cells are found along the hypoglossal nerve (XII) and close to the sixth pharyngeal arch artery (a6). (C) Three‐dimensional reconstruction of the head–trunk interface in an Oryzias latipes hatchling. Note that the cleithrum develops attached to the hypoglossal nerve. (D) Schematic drawing shows the heterotopic transplantation. The quail head mesoderm was transplanted into the place of LPM adjacent to somites 1–3 in the chicken host. (E–E''') Transverse section of chick–quail chimera at HH stage 34+, in which LPM beside somites 1–3 were homotopically replaced with that of the donor quail, showing the distribution of the cucullaris muscle (cc). (E'–E''') are higher magnifications of the box in (E). Note that QCPN‐positive quail nuclei (arrow heads) are found in the myosin heavy chain (MyHC) positive cucullaris myofibers (E'–E'''). (F–F''') Transverse section of chick–quail chimera at HH stage 34+, in which the quail head mesoderm was heterotopically transplanted, as shown in (D). (F'–F''') are higher magnifications of the box in (F). Note that the head mesoderm formed the cucullaris muscle with normal morphology (F), and that QCPN‐positive quail nuclei (arrowheads) are found in the MyHC‐positive cucullaris myofibers (F'–F'''). (G,H) Transverse section of the clavicle in the heterotopic head mesoderm chimera. (H) is an adjacent section to (G). Note that QCPN‐positive quail cells contribute to the clavicle. Abbreviations: cb3–5, ceratobranchials 3–5; ccv, common cardinal vein; cr, crop; da, dorsal aorta; eca, external carotid artery; ed, endoskeletal disc; ica, internal carotid artery; m, mesencephalon; p, prosencephalon; ph, pharynx; pp, postcoracoid process; r, rhombomere; so, scapulocoracoid; var, ventral aortic root; X, vagus nerve. Scale bars: 50 μm (B); 20 μm (G and H).
