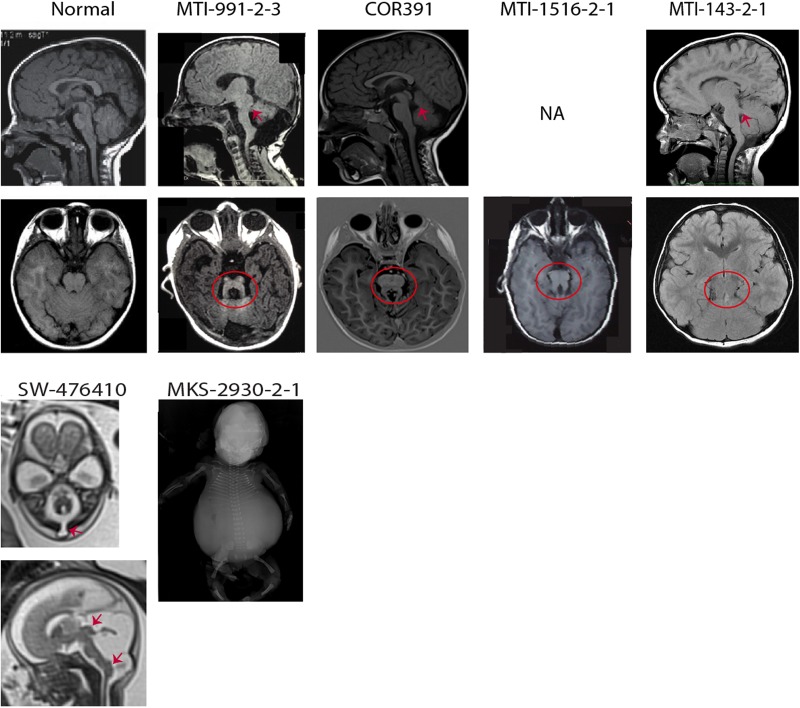
Figure 2.
Neuroimaging or neuropathological findings of probands with CEP120 mutations are shown. Upper panel: Sagittal T1-weighted and axial T1-weighted/coronal fluid attenuation inversion recovery MRIs of a healthy subject and patients with Joubert syndrome (JS) having CEP120 mutations show thickened and maloriented superior cerebellar peduncle (upper arrows in MTI-991-2-3 and MTI-143-2-1), rostral shifting of the fastigium of the fourth ventricle (upper arrow in COR391), deepened interpeduncular fossa and constituting the ‘molar tooth sign’ (circled). Lower panel: SW-476410: axial and midsagittal T2-weighted fetal MRIs at 23 weeks of gestation show a suboccipital encephalocele (arrow on the axial image), severe hypoplasia of the cerebellar vermis and tectal dysplasia (upper arrow on the sagittal image) consistent with the diagnosis of tectocerebellar dysraphia with occipital encephalocele (TCDOE). In addition, enlargement of the posterior fossa and dorsal protuberance of the lower brainstem (lower arrow on the sagittal image) are noted; Meckel syndrome (MKS)-2930-2-1: a fetogram after termination of pregnancy in the second trimester reveals a marked abdominal distention, a narrow bell-shaped thorax with short ribs, rhizomelic limb shortening and bowing of long bones.