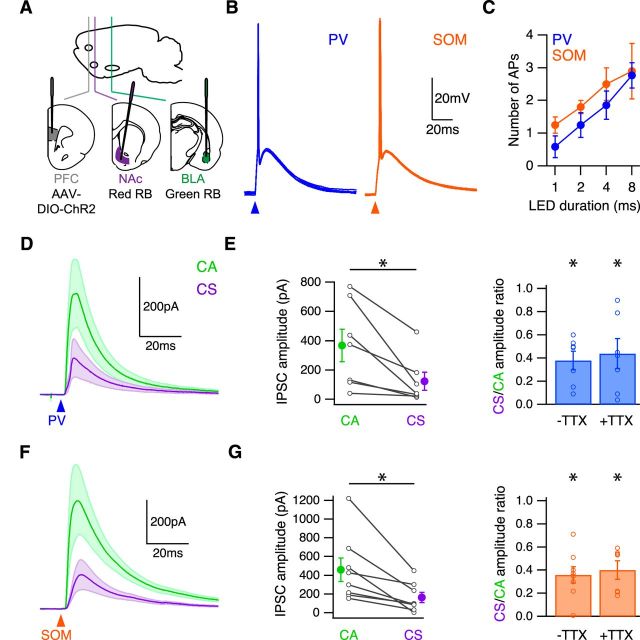
Figure 5.
PV and SOM inhibition is stronger at CA neurons. A, Schematic of injecting AAV-DIO-ChR2-eYFP into the infralimbic PFC, red retrobeads into the NAc, and green retrobeads into the BLA of either PV-Cre or SOM-Cre mice, to express ChR2 in either PV or SOM interneurons and label CS and CA neurons in the PFC. B, Light-evoked AP firing in PV (blue) and SOM (orange) interneurons expressing ChR2 in the presence of NBQX and CPP, showing multiple trials at a 1 ms LED duration. Arrowheads indicate time of LED pulse. C, Summary of AP firing over range of LED durations for PV and SOM interneurons. D, Average GABAA-R IPSCs evoked by PV interneurons (blue arrowhead) in the presence of NBQX and CPP. E, Summary of amplitudes of PV-evoked IPSCs at CA and CS neurons (left). Lines connect pairs of recorded neurons. Summary of CS/CA amplitude ratio in the absence (−) or presence (+) of TTX and 4-AP (right). F, Average GABAA-R IPSCs evoked by SOM interneurons (orange arrowhead) in the presence of NBQX and CPP. G, Summary of amplitudes of SOM-evoked IPSCs at CA and CS neurons (left). Lines connect pairs of recorded neurons. Summary of CS/CA amplitude ratio in the absence (−) or presence (+) of TTX and 4-AP (right). *p < 0.05.