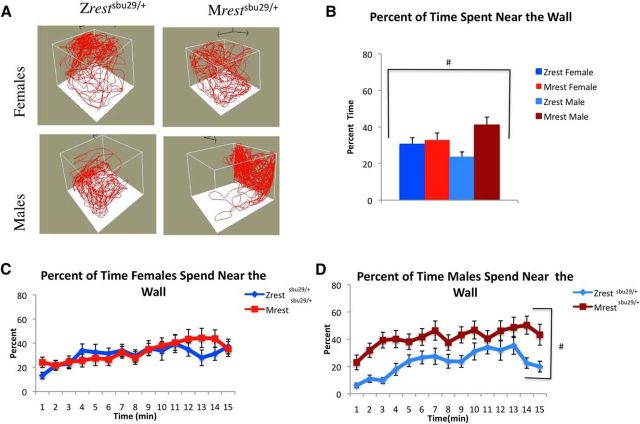
Figure 6.
Mrestsbu29/+ males, but not females, showed increased wall preference in the novel environment assay. A, Locomotion diagrams for individual fish over 5 min showing the Mrestsbu29/+ male wall preference. B, During the assay, Mrestsbu29/+ (N = 21) males spent more time near the wall compared with Zrestsbu29/+ (N = 20) controls. C, D, Analysis of percentage of time spent near the walls for females (Mrestsbu29/+, N = 18; Zrestsbu29/+, N = 20) (C) and males (D) in 1 min intervals reveals that Mrestsbu29/+ males, but not females, tend to swim near the side of the tank over the entire assay. Significance was defined using a multivariate ANOVA to identify main effects of sex and/or genotype and significant interactions between the two over the testing period. A two-way repeated-measures ANOVA was also used to compare within-sex data collected in 1 min bins across the 15 min testing period. #Genotype (p < 0.05).