FIG 1 .
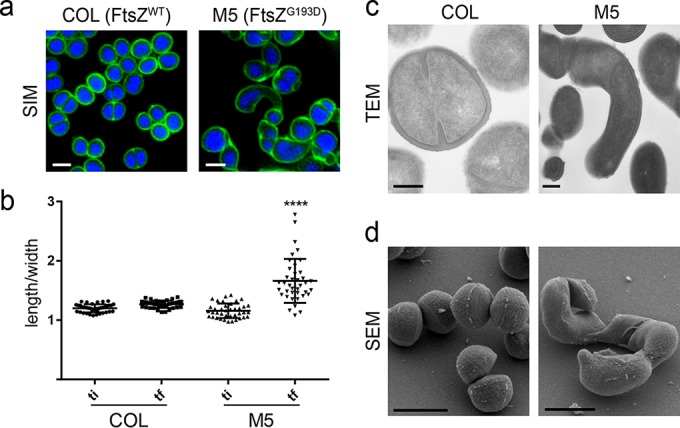
The FtsZG193D mutation leads to S. aureus cell elongation. (a) SIM images of wild-type COL (left) and FtsZG193D mutant M5 (right) cells labeled with the cell wall dye Van-FL (green) and the DNA dye Hoechst 33342 (blue). Scale bar: 1 µm. (b) The ratio of the longer to the shorter axis was calculated at two time points during the cell cycle, an initial time point (ti) when cells had a round shape and a final time point (tf) when cells were most elongated, prior to splitting of the mother cell. M5 cells elongate significantly more during the cell cycle than COL wild-type cells (P < 0.001). (c) Transmission electron micrographs (TEM) of thin sections of COL and M5 cells. Scale bars: 200 nm. (d) Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of COL and M5 cells. Scale bars: 1 µm.
