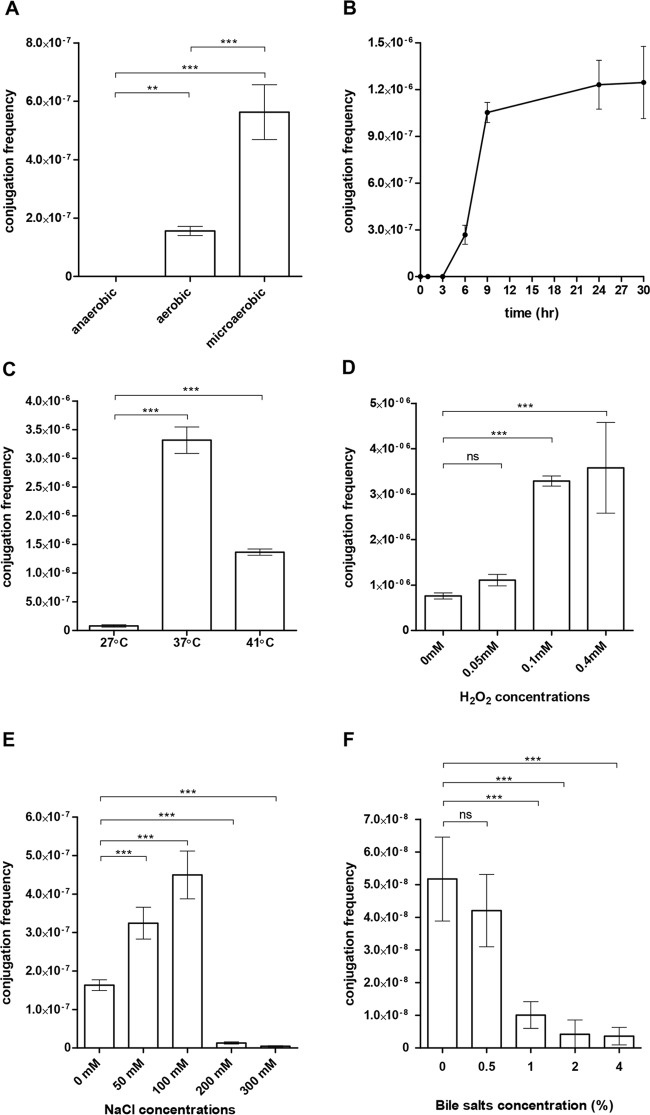
FIG 3 .
pESI conjugation is increased in response to microaerobiosis, physiological temperature, and moderate osmolarity. The pESI conjugation frequency (obtained transconjugants/donor CFU) between S. Infantis 119944 (donor) and E. coli ORN172 (recipient) was determined under (A) different oxygen conditions, (B) over time under a microaerobic environment, and at different (C) temperatures, (D) hydrogen-peroxide concentrations, (E) sodium chloride concentrations, and (F) bile salt concentrations. Bars show the means and SDs from at least four independent mating experiments. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s (for panels A and C) or Dunnett’s (for panels D to F) multiple comparison tests was implemented to determine statistical significance. ns, not significant; **, P < 0.001; ***, P < 0.0001.