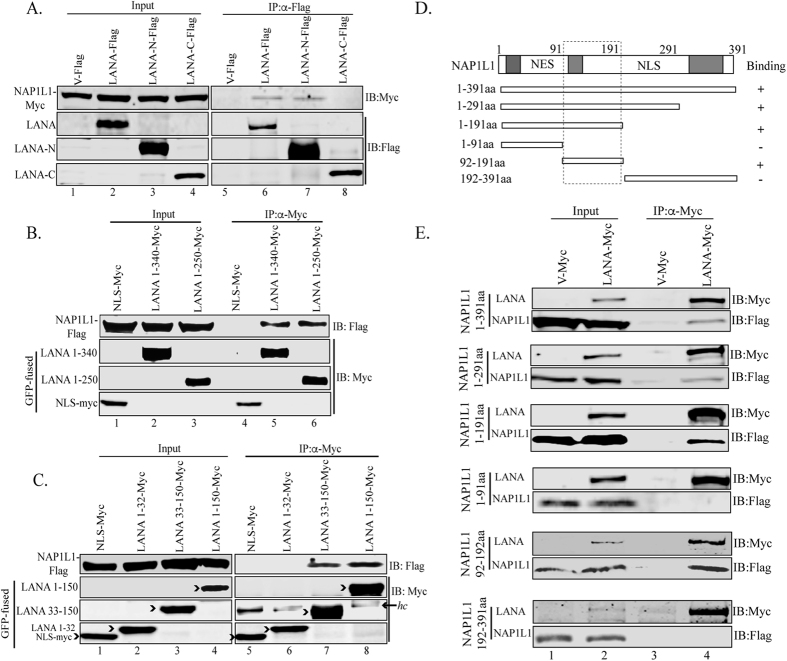
Figure 3. The amino terminus of LANA interacted with NAP1L1 in the acidic domain.
(A) HEK 293T cells were transfected with Flag-tagged pA3F empty vector, pA3F LANA, pA3F LANA-N and pA3F LANA-C along with Myc-tagged NAP1L1. The lysate was subjected for immunoprecipitation with anti-Flag antibody followed by detection with anti-Myc antibody, which shows binding with full length and the amino terminal domain (lanes 6 and, 7) but not with control (lane 5) or carboxy terminal domain (lane 8). (B,C) HEK 293T cells were transfected with GFP-NLS-Myc (empty vector), LANA truncation spanning aa 1 to 340 (LANA 1-340)-GFP-Myc, LANA 1-250-GFP-Myc, LANA 1-150-GFP-Myc, LANA 33-150-GFP-Myc, or LANA 1-32-GFP-Myc along with Flag-tagged NAP1L1. Cell lysates were subjected to IP with anti-Myc antibody to detect co-immunoprecipiated NAP1L1. LANA aa 1-340, aa-1-250, 1-150 and 33-150 bound to NAP1L1. hc represents the heavy chain of the antibody. (D) Schematic of NAP1L1 truncation domains and its binding summary to LANA. The acidic domains of the protein are shown by grey boxes and the NES and NLS are the nuclear export and nuclear localization signals, respectively. (E) HEK 293T cells were cotransfected with pA3M empty vector, pA3M LANA along with Flag-tagged NAP1L1 aa 1 to 391, NAP1L1 aa 1 to 291, NAP1L1 aa 1 to 191, NAP1L1 aa 1 to 91, NAP1L1 aa 92 to 191 and NAP1L1 aa 192 to 391. The cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc antibody to detect the NAP1L1 truncations with anti-Flag antibody (lane 4 in each panel).