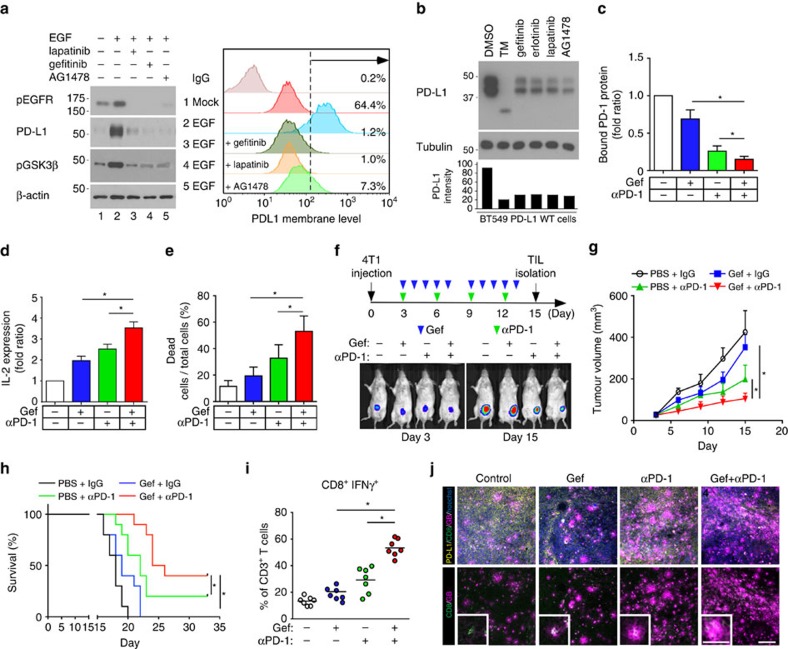
Figure 5. Inhibition of EGFR sensitizes the PD-1 blockade therapy in syngeneic mouse model.
(a) Cells were treated with TKIs for 2 h before EGF stimulation. Cell surface analysis of PD-L1 protein using flow cytometer was shown in the right. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 protein in the cells treated with several indicated inhibitors. PD-L1 WT-expressing BT549 cells were treated with 1 μg ml−1 TM, 1 μM gefitinib, 1 μM erlotinib, 1 μM lapatinib and AG1478. (c) PD-L1 and PD-1 interaction in PD-L1-expressing BT549 cells. (d) Soluble IL-2 levels in PD-L1-expressing BT549 cells treated with gefitinib and/or anti-PD-1 antibody. (e) T-cell-meditated killing of PD-L1-expressing BT549 cells treated with gefitinib and/or anti-PD-1 antibody. (f) The tumour growth of 4T1-Luc cells in BALB/c mice following treatment with gefitinib and/or anti-PD-1 antibody. Treatment protocol is summarized (top). Tumour growth of 4T1-Luc cells was shown in vivo by bioluminescence imaging using IVIS100 (bottom). (g) The tumour growth of 4T1 cells in gefitinib- and/or anti-PD-1 antibody-treated BALB/c mice. Tumours were measured at the indicated time points and dissected at end point. Quantification of tumour volume is shown on the right and representative images of tumours are shown on the left. n=9 mice per group. (h) Survival of mice bearing syngeneic 4T1-Luc-derived tumour following treatment with gefitinib and/or anti-PD-1 antibody. Significance was determined by log-rank test. *P<0.05; n=10 mice per group. (i) Intracellular cytokine stain of IFNγ and CD8 in CD3+ T-cell populations from the isolated tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes. (j) Immunofluorescence staining of the protein expression pattern of PD-L1, CD8 and granzyme B (GB) in 4T1 tumour mass. *P<0.05 is statistically significant as shown by Student's t-test. All error bars are expressed as mean±s.d. of three independent experiments. Gef, gefitinib.